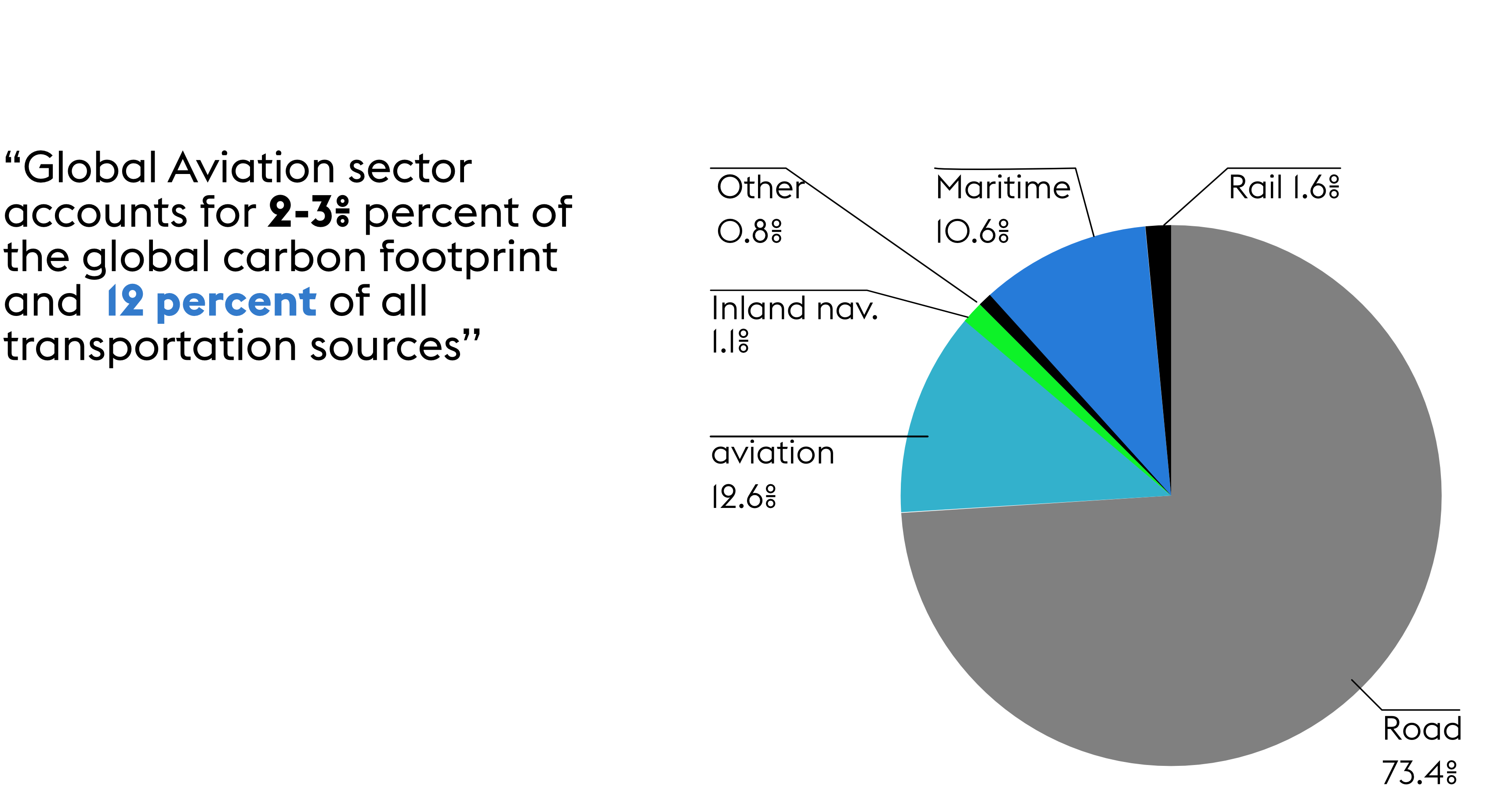Maximum value
for the minimum mass.
SKY
Lightweight
and sustainable airline seat
TU-Delft - 2021
Master Graduation Thesis
Integrated Product Design
Summary
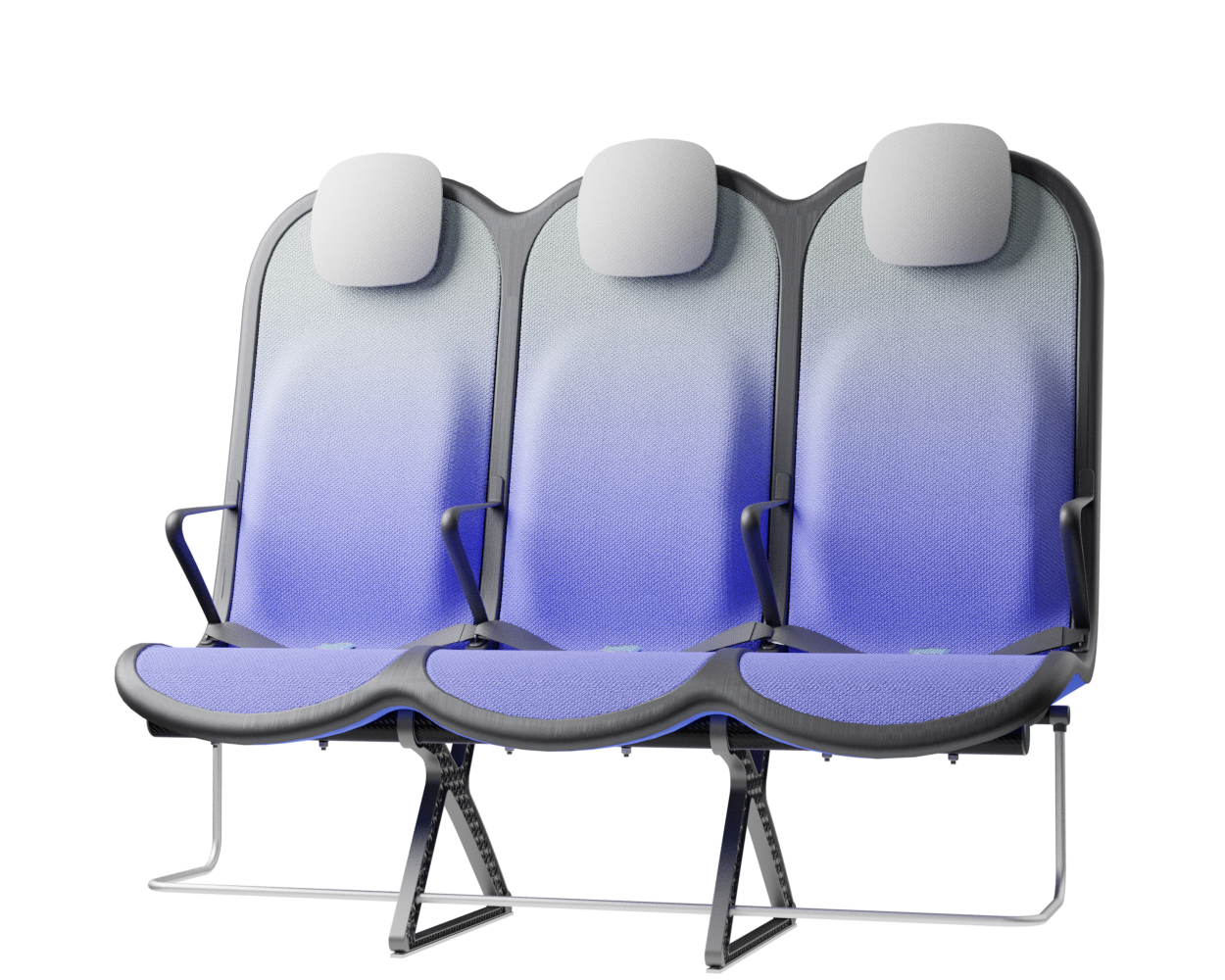
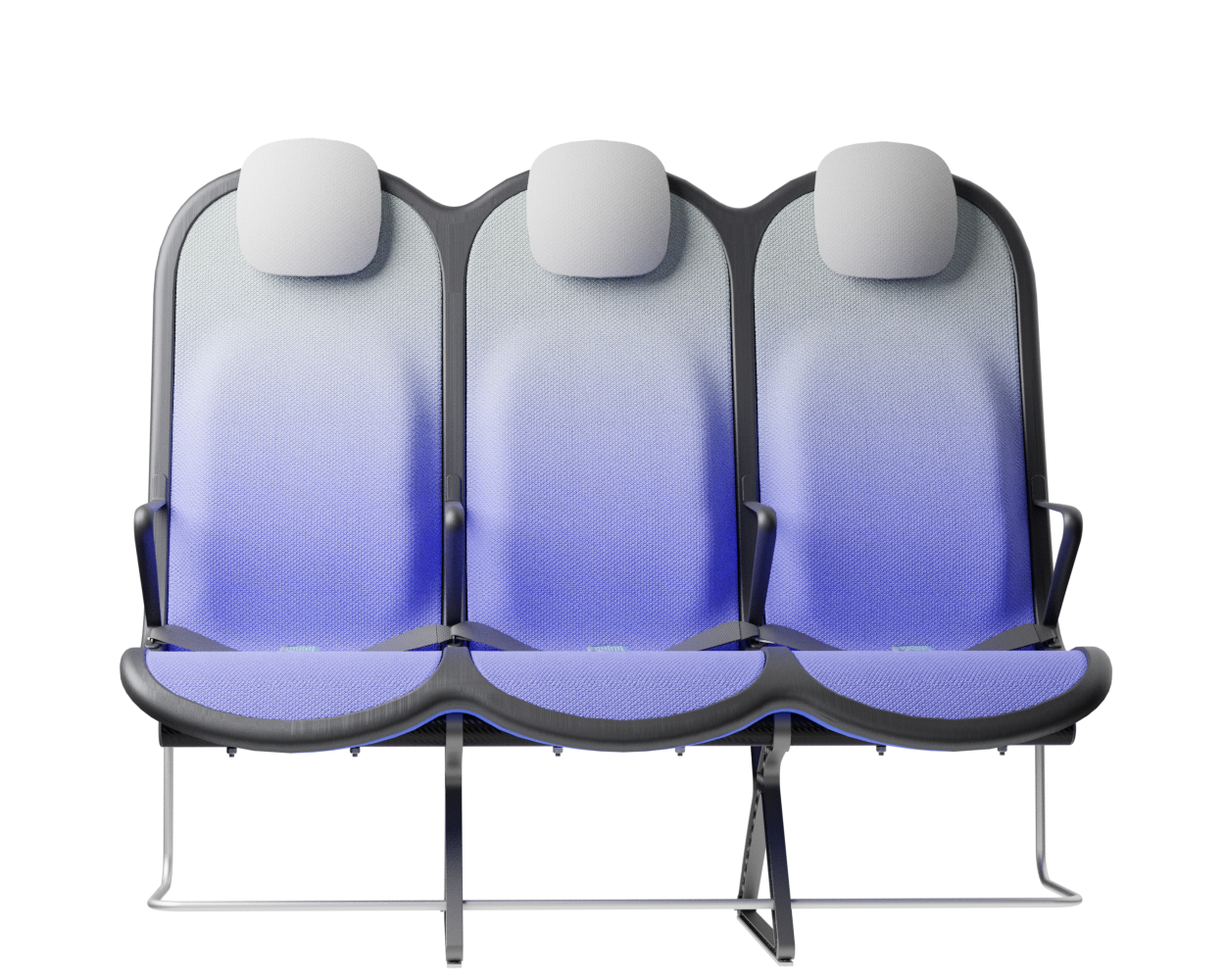
Weight reduction is one of the critical factors in making commercial aviation more sustainable. This project focuses on aircraft efficiency by developing a lightweight aircraft seat for the economy segment during short-haul flights. The result of this thesis project is a concept proposal for a 3-seater bench with a per-seat weight of approximately 6.5 kg. The low weight is achieved by addressing the structure of the seat with a single-part compression-moulded shell made of CFRTP, consolidating conventional multi-component assemblies, while comfort is provided by replacing traditional PU foams with a lightweight fabric suspension system.
DESIGN PROCESS
Discover
Project motivation




“Designing maximum value for minimum amount of mass’’
+
“Creating Synergy between passengers, the airline and the environmental needs.’’
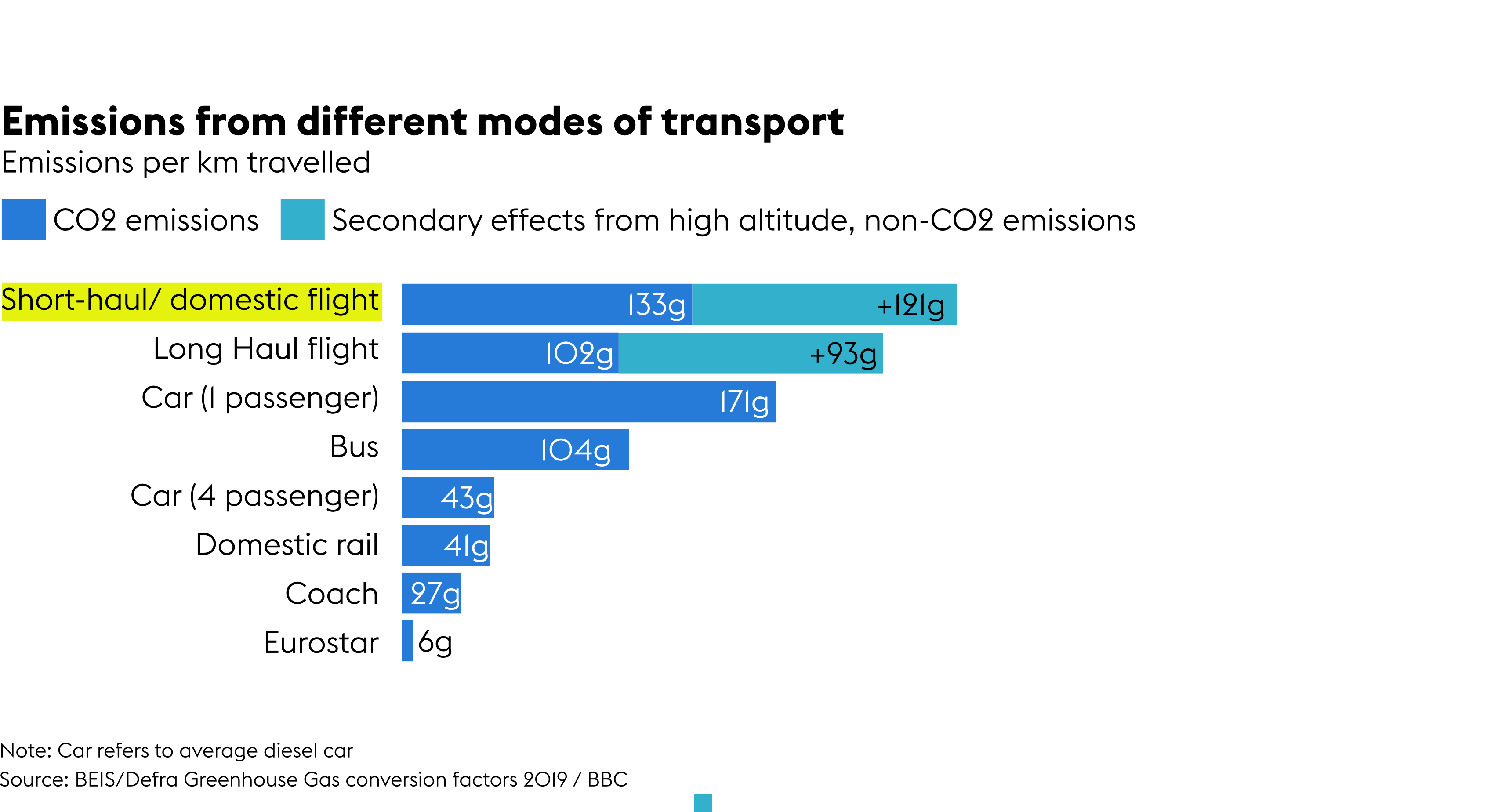
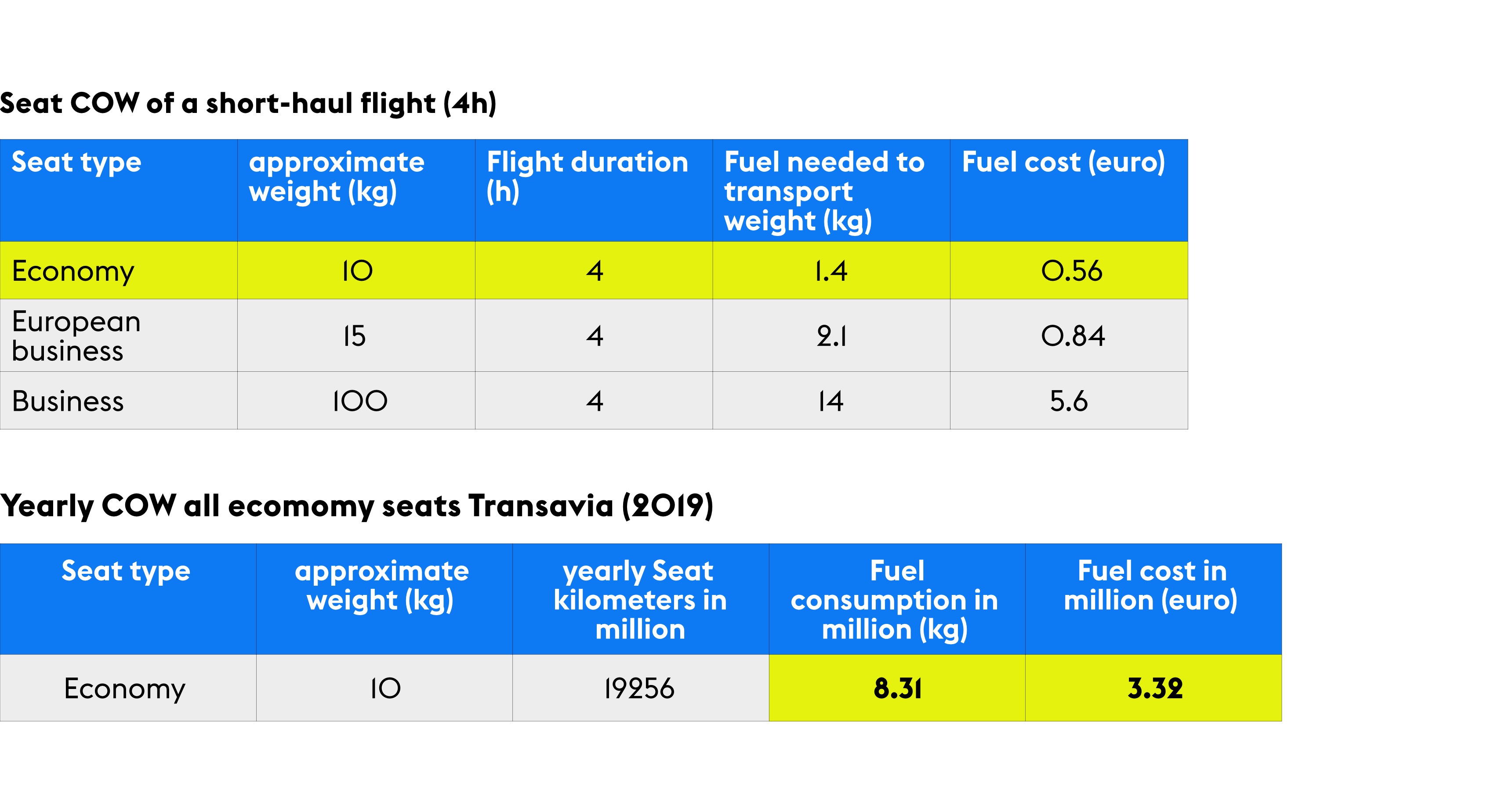
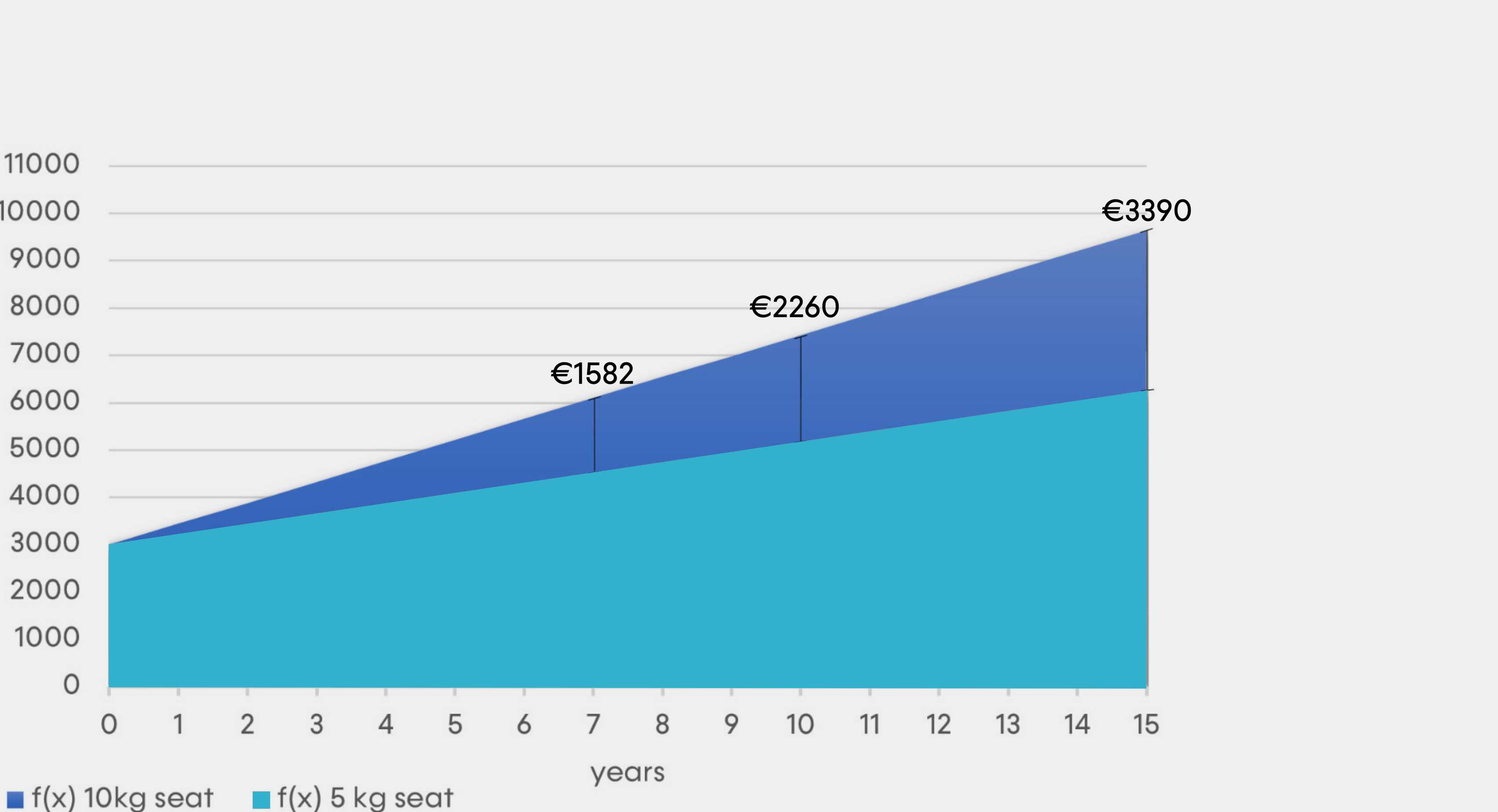
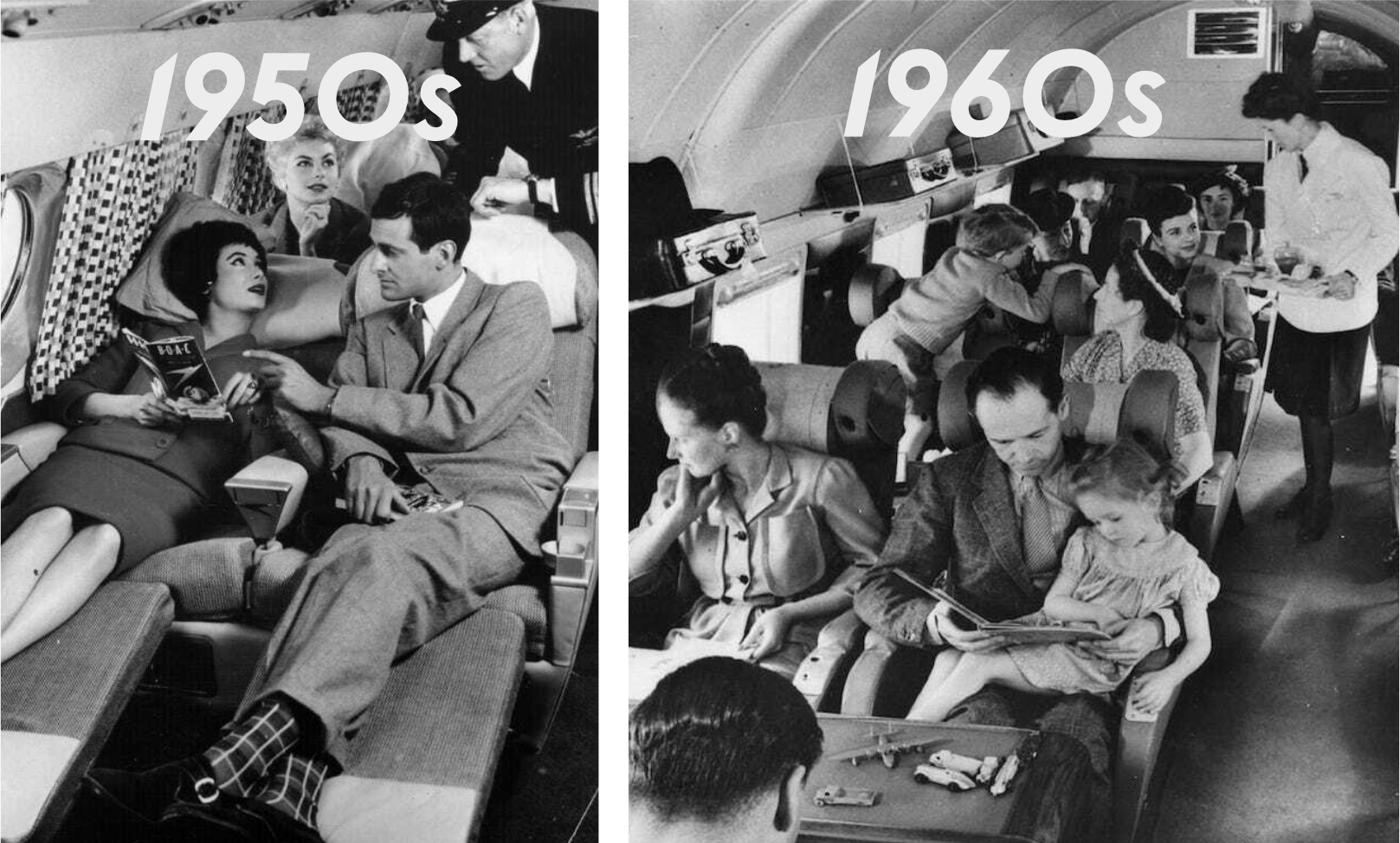
Sustainability of flying
Seat weight breakdown
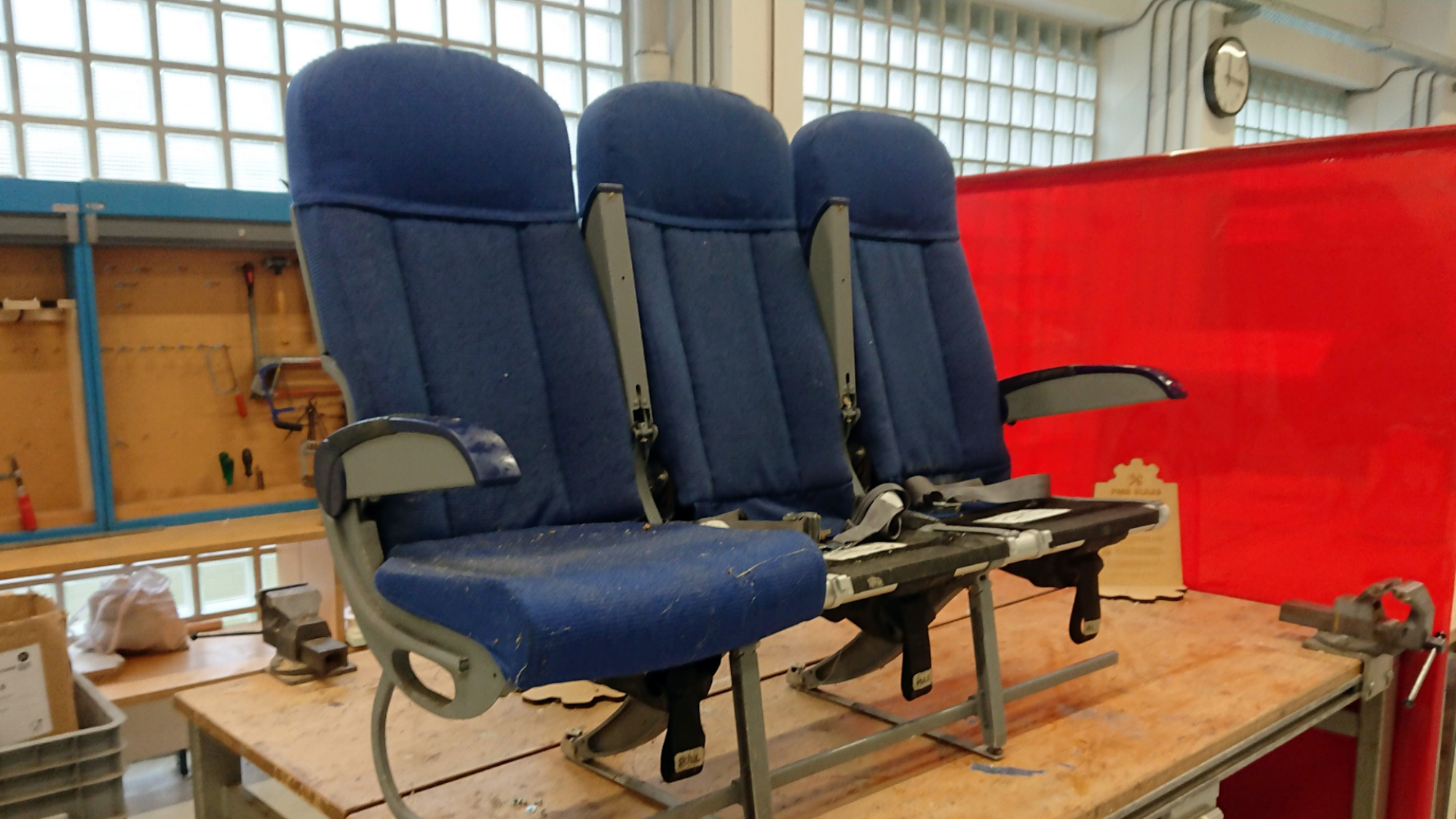
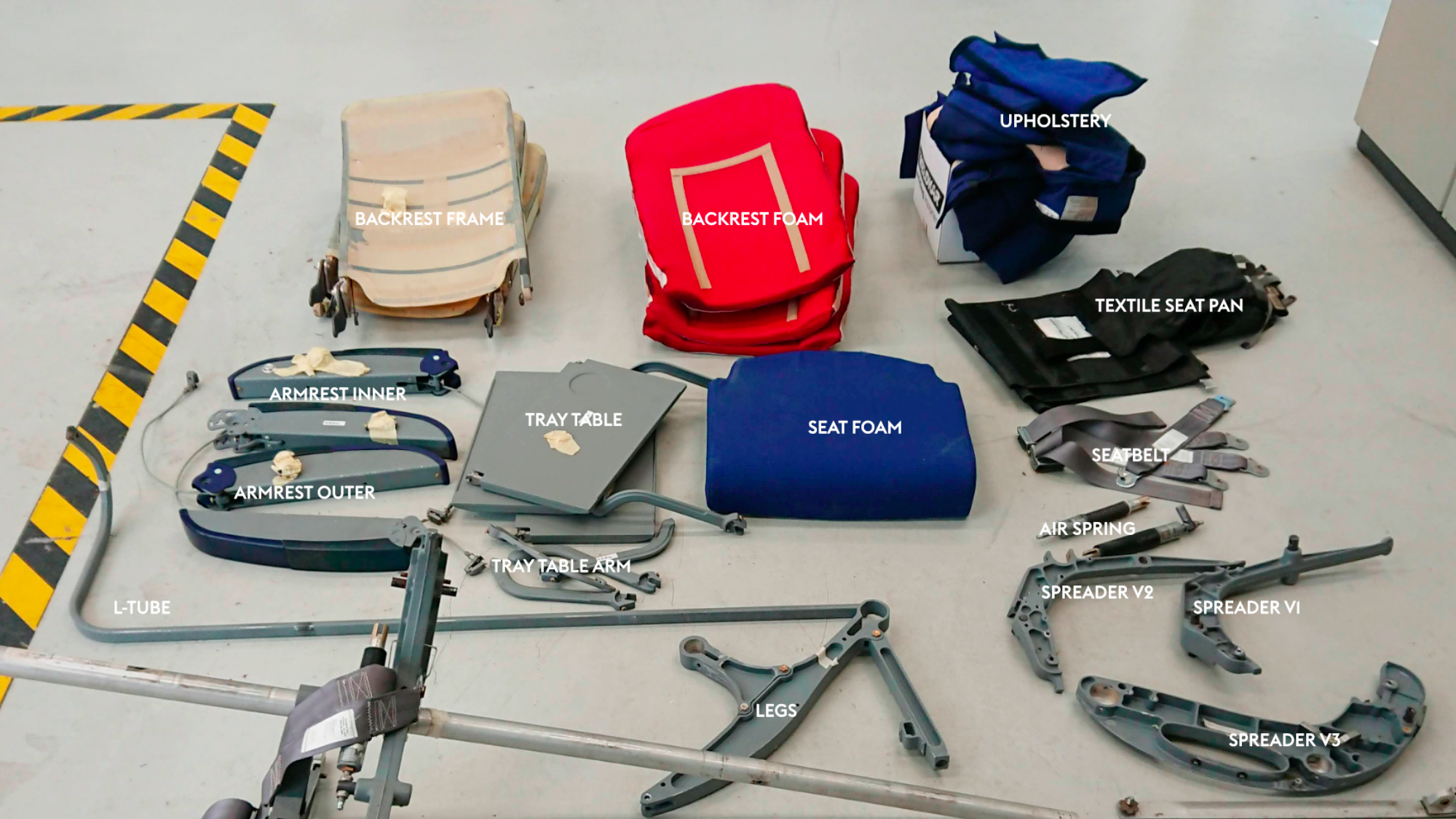


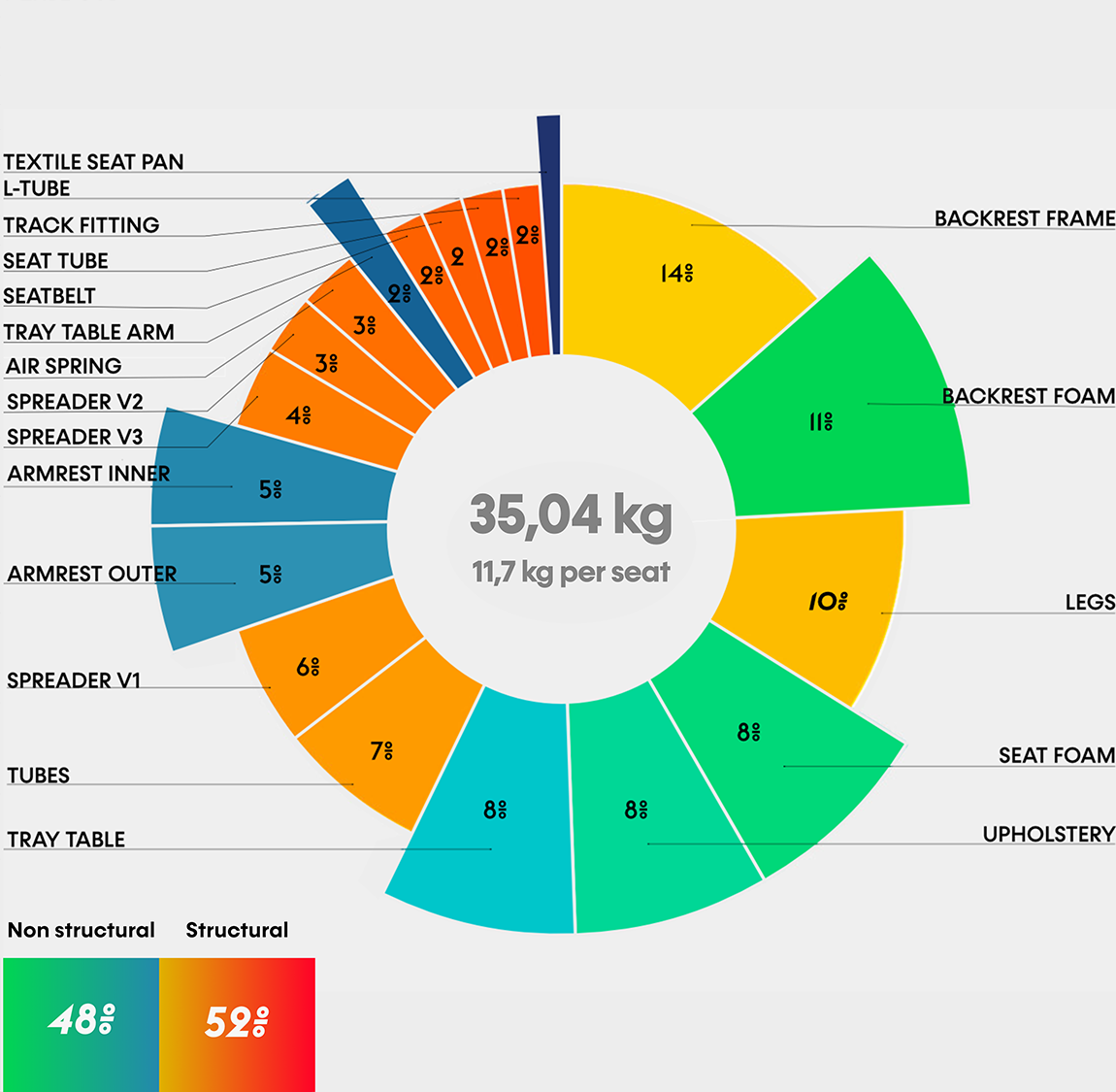
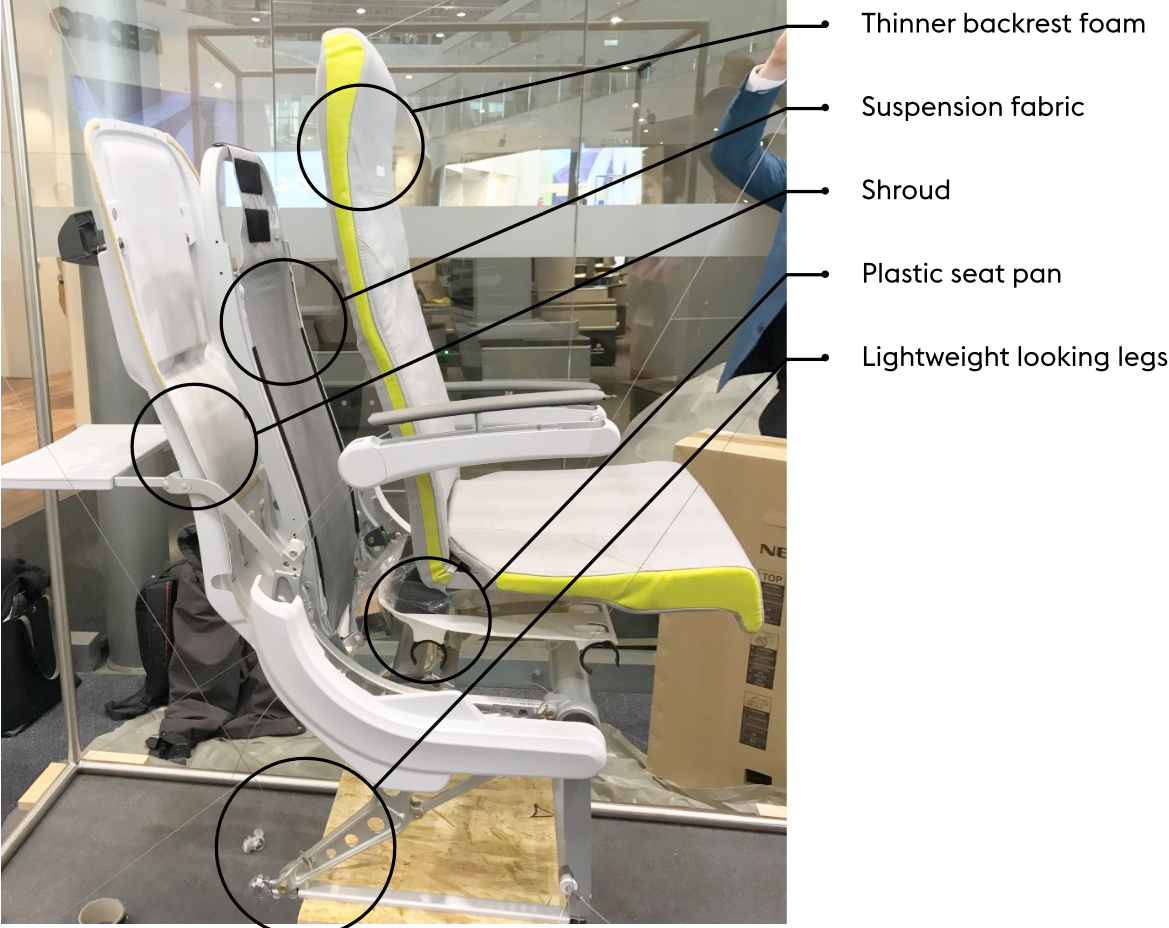
An economy airline seat was disassembled to gain insight into the seat components with the most room for weight savings.
With non-structural components accounting for 48% of the total weight, there is clear room for significant weight savings by tackling areas such as the seat foams and upholstery and rethinking the way comfort is provided.
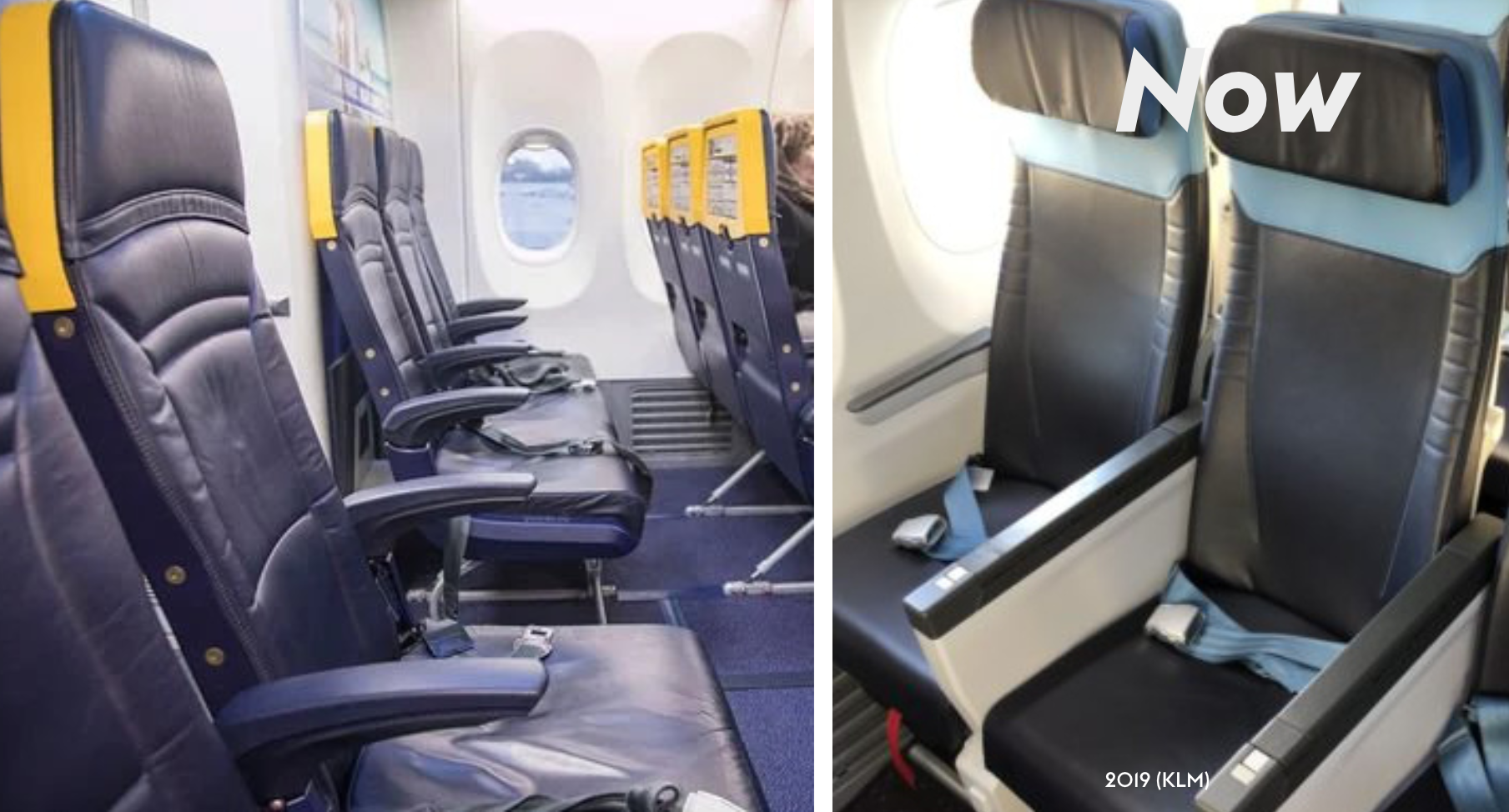
Contemporary Seats:
Weight benchmarking
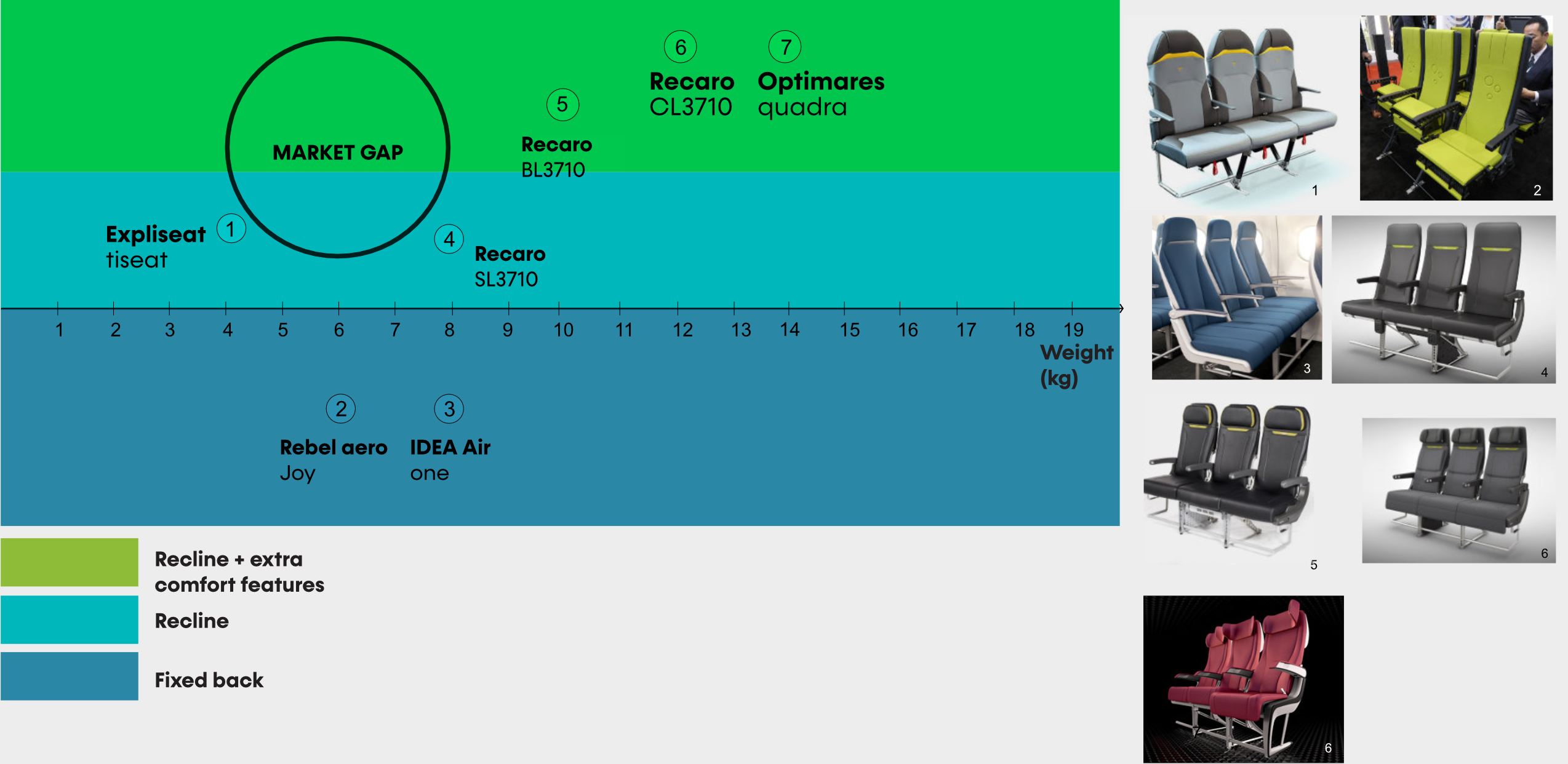

Explore
Ideation sketches

Define & test
Concept 1
What?
The first concept was inspired by lightweight carbon fibre bicycle frames.
The idea was to create a lightweight frame that acts as a structural exoskeleton.
On this exoskeleton, a lightweight aluminium frame supports the passenger from a suspension fabric. In this concept the pivot point of the recline is placed at the top of the carbon frame; this enables the passenger to tilt forward into a cradle position so that, when the passenger leans back, the rear passenger's personal space is not compromised.
advantages vs disadvantages
+ Smaller pitch possible due to frame geometry
+ Integration of structural parts and functions into one component
- The production method of carbon composite frames is labour intensive
- Thermoset resin is not recyclable
- Recline mechanism requires forces higher than current mechanisms
Concept 2
What?
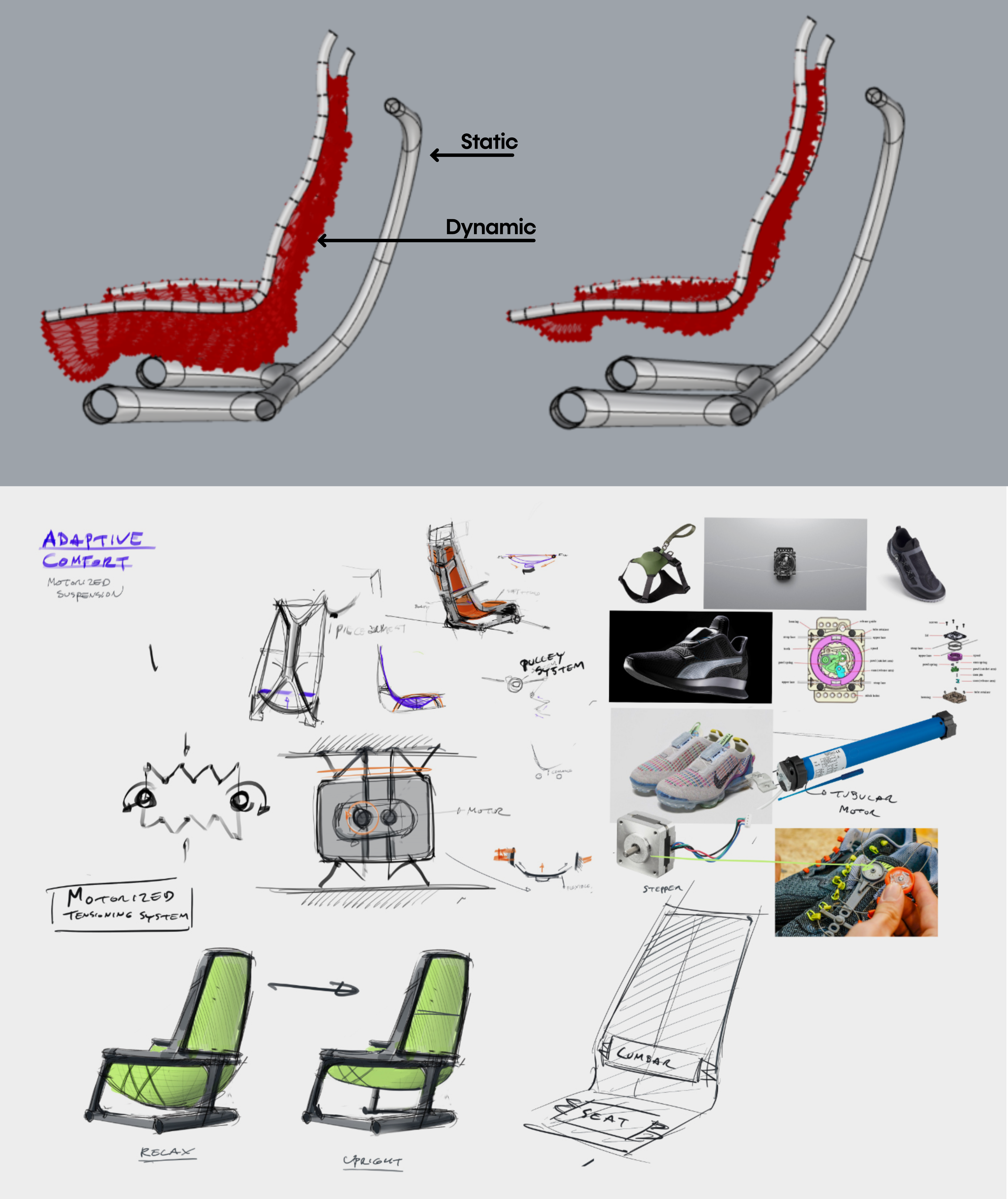
The second concept moves away from a frame with moving parts to a fixed structure with the possibility of changing position by adjusting the tension of the textile mesh using a mechanism.
Numerous mechanisms were explored however, it quickly became apparent that a motorized system would be needed. This would require seat- electricity, which is a rarity on short-haul flights and adds extra weight to the aircraft. Also, the forces to lift someone up in the seat would require high torque motors making the overall seat heavier.
While this could have been an interesting direction for other types of seating such as business class, it didn't fit with the most important rule of lightweight design: to not over-specify and strive to ensure that the product does exactly what it is supposed to and do nothing more than that.
advantages vs disadvantages
- In-seat electricity will add weight to the aircraft.
+ Fixed frame structure gives the opportunity for lightweighting
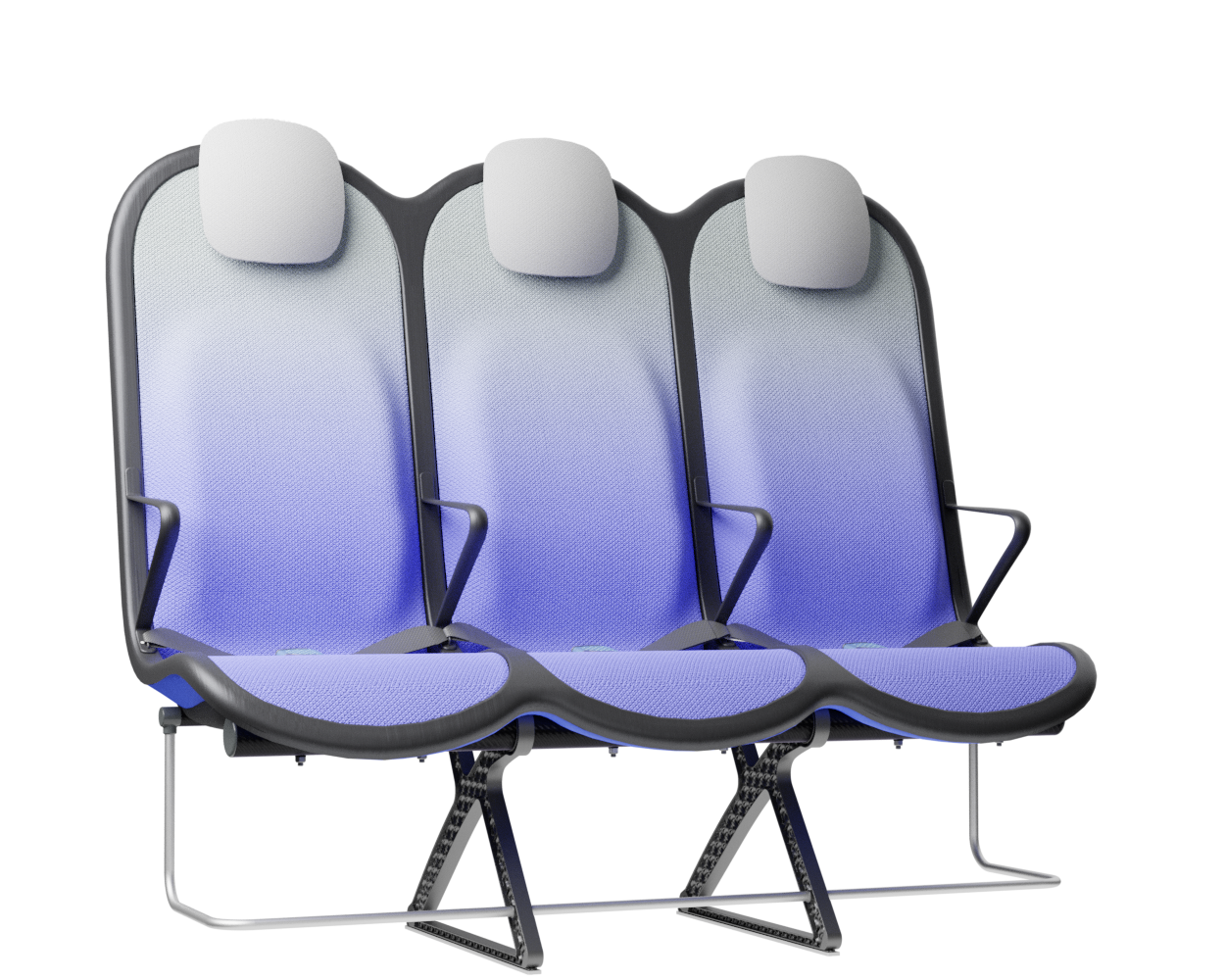
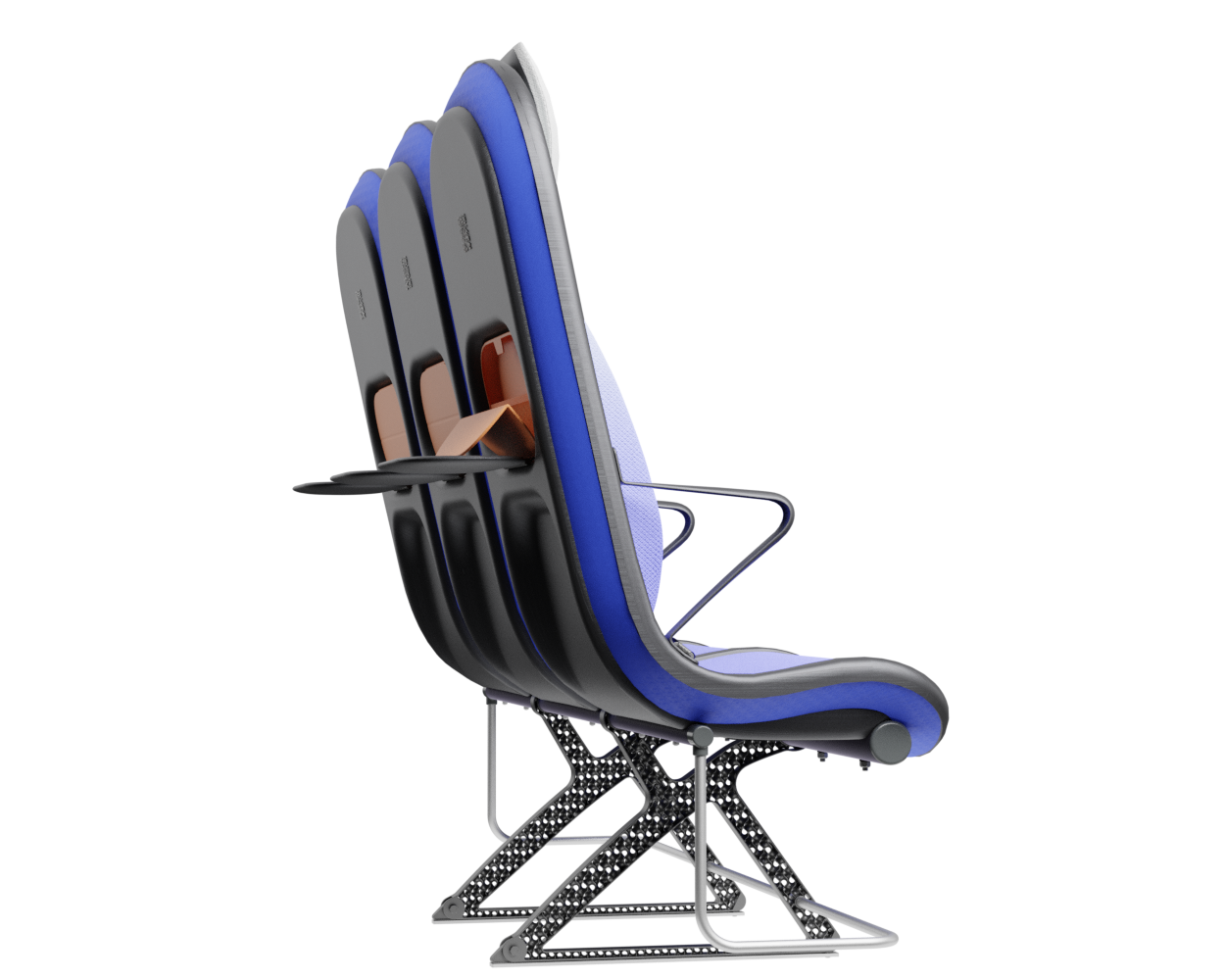
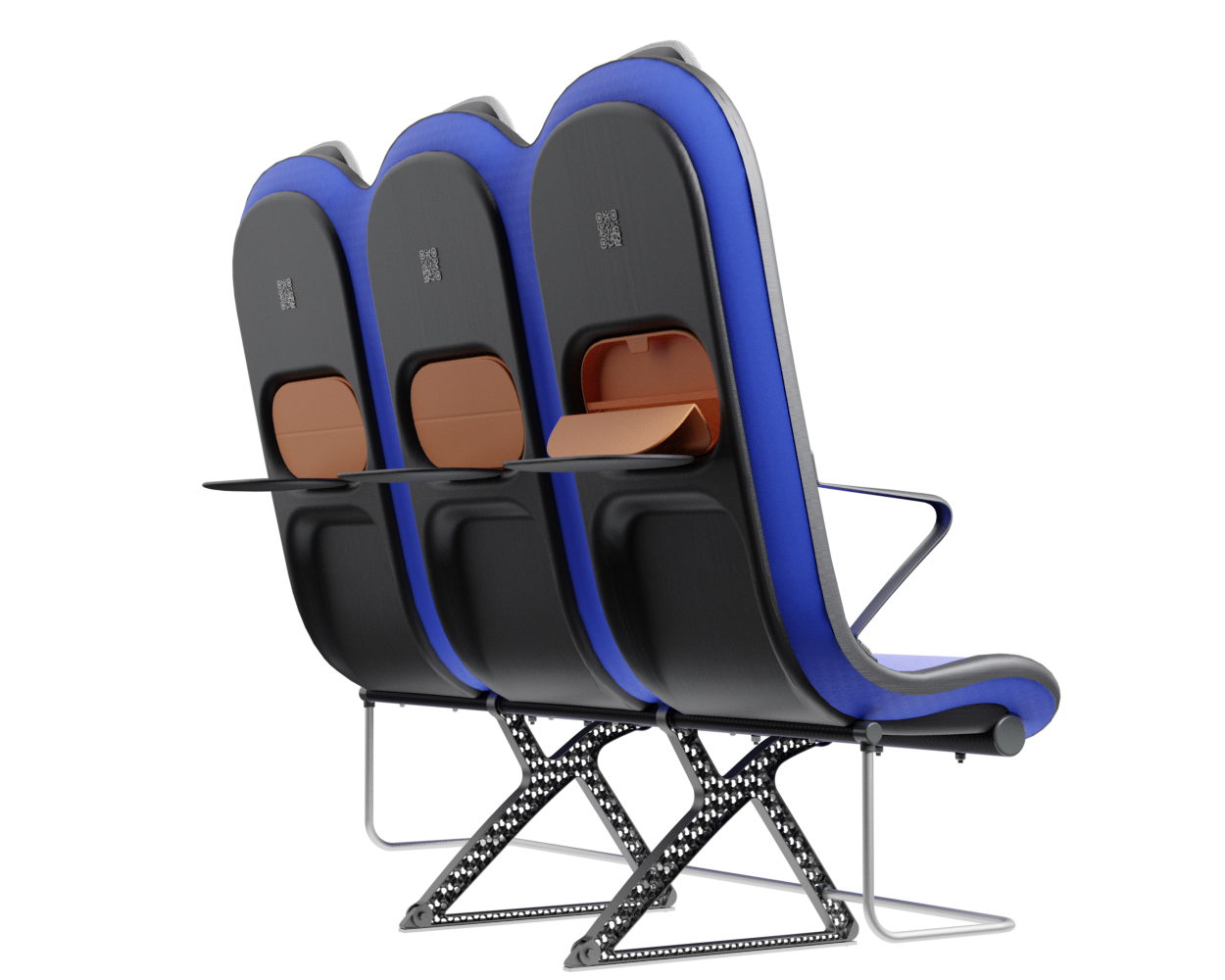
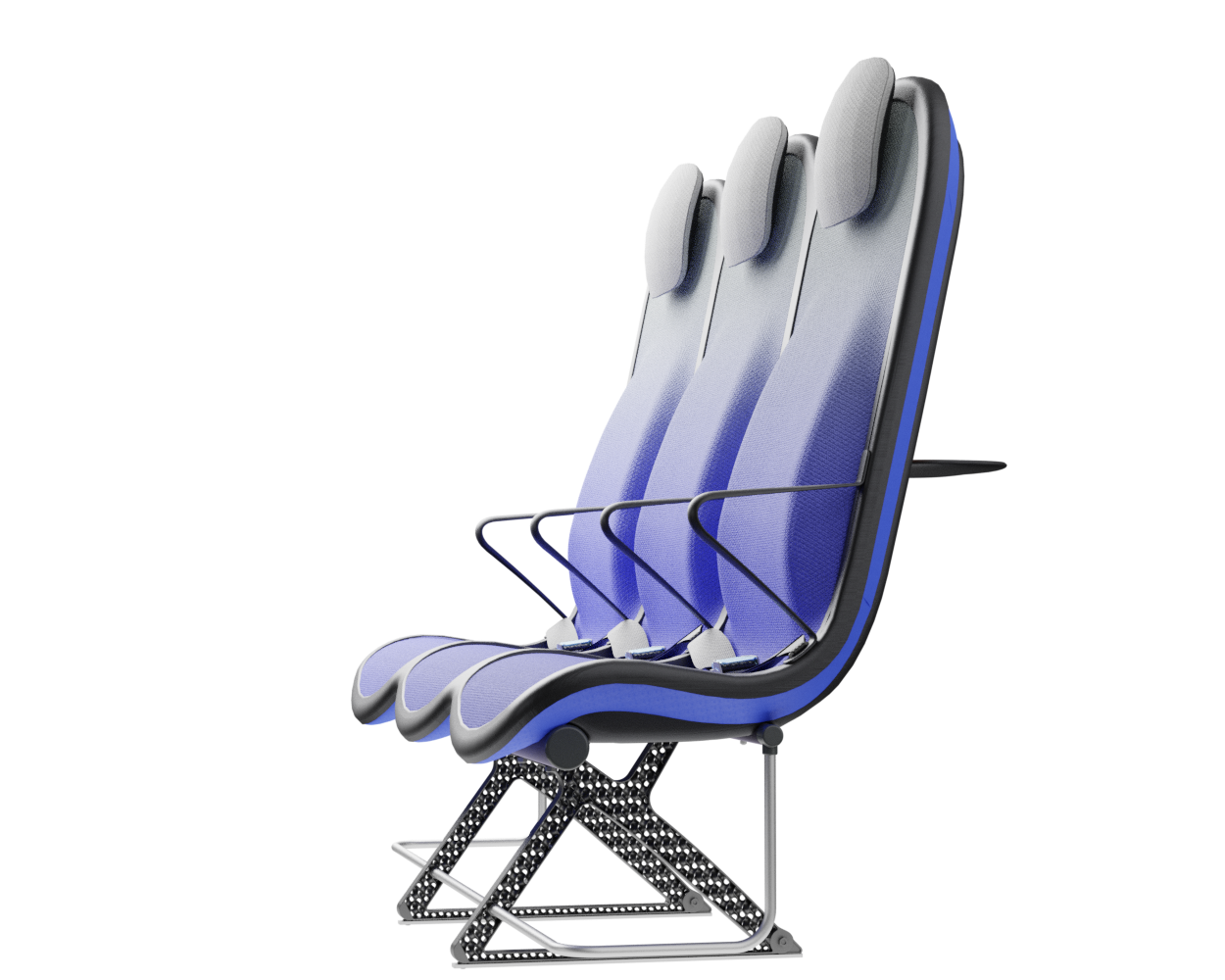
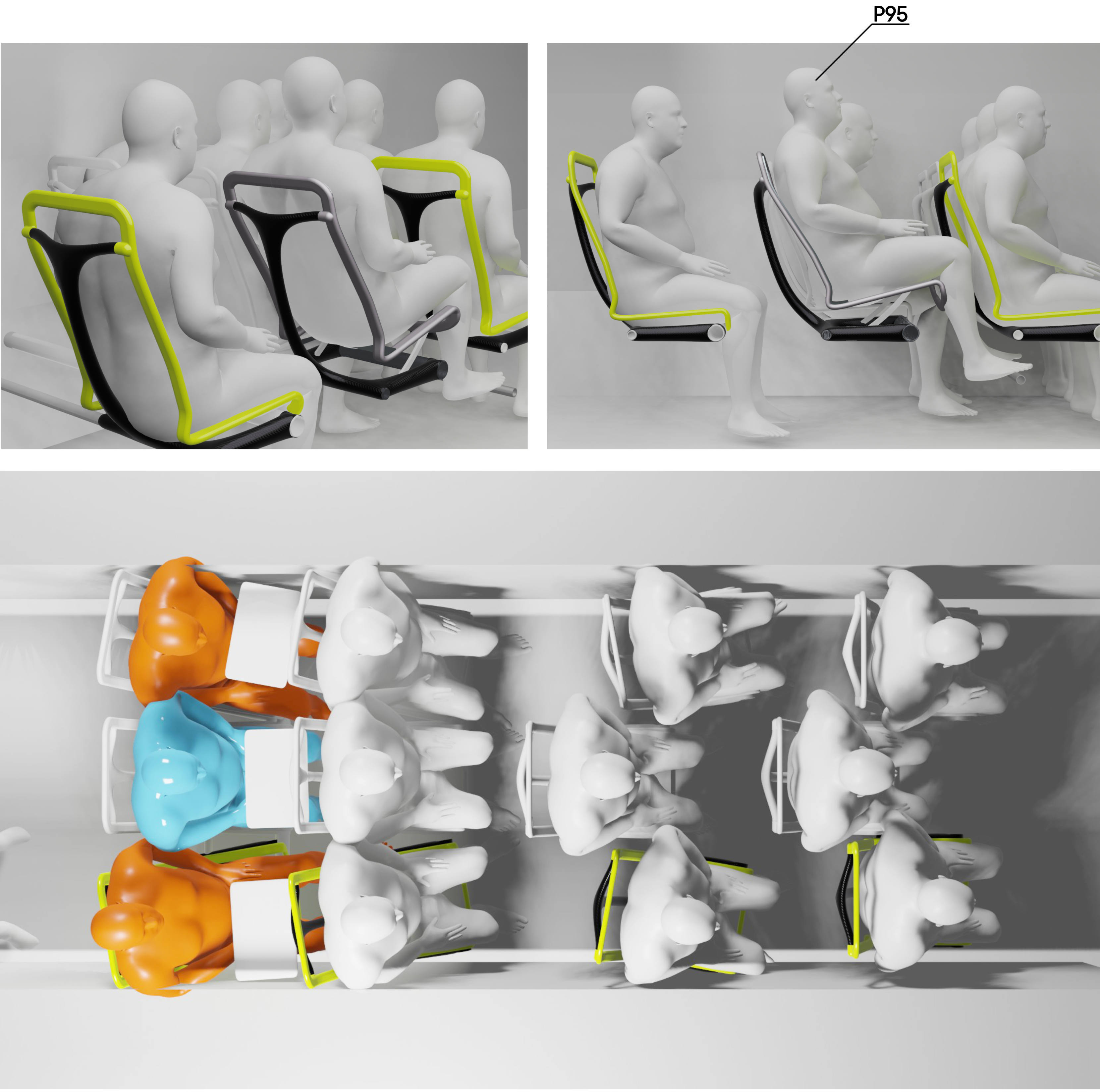
Final concept!

What?
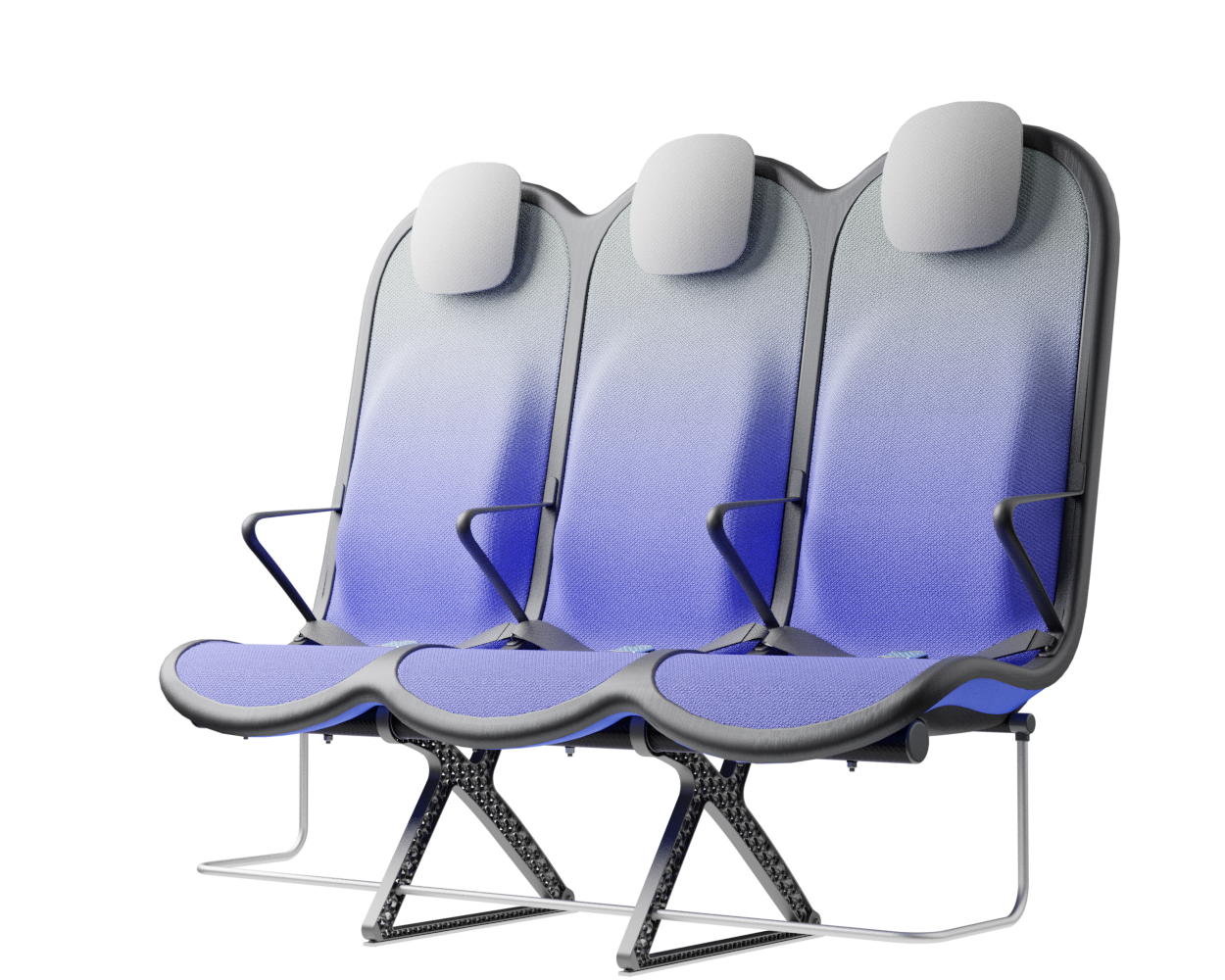
The third and final concept direction addresses the problems of the previous two concepts by finding a solution for a lightweight structure suitable for mass production and seating comfort without complicated mechanisms or electricity necessities. Since structure and comfort are the main areas addressed in the concept, the concept description will first address these areas.
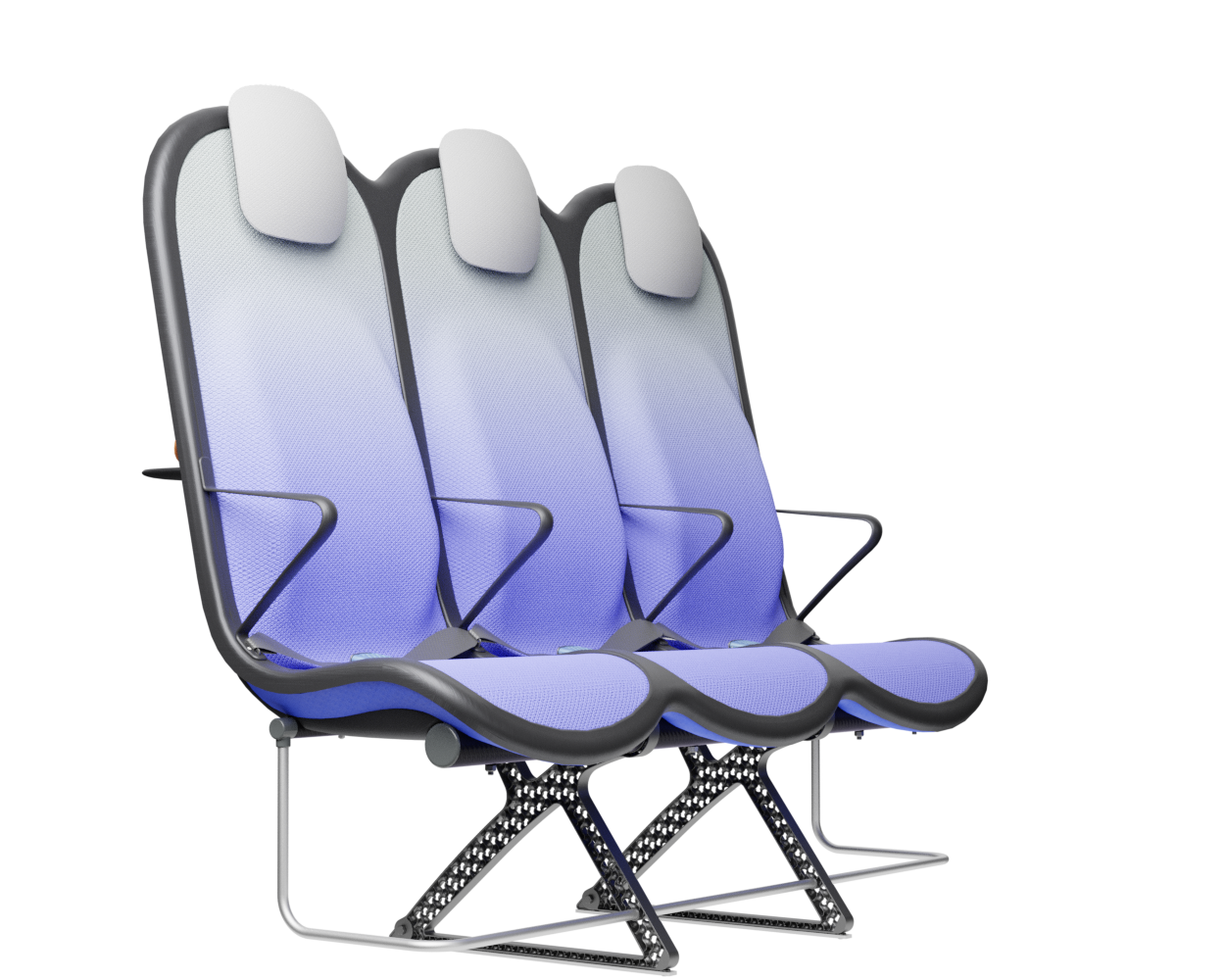
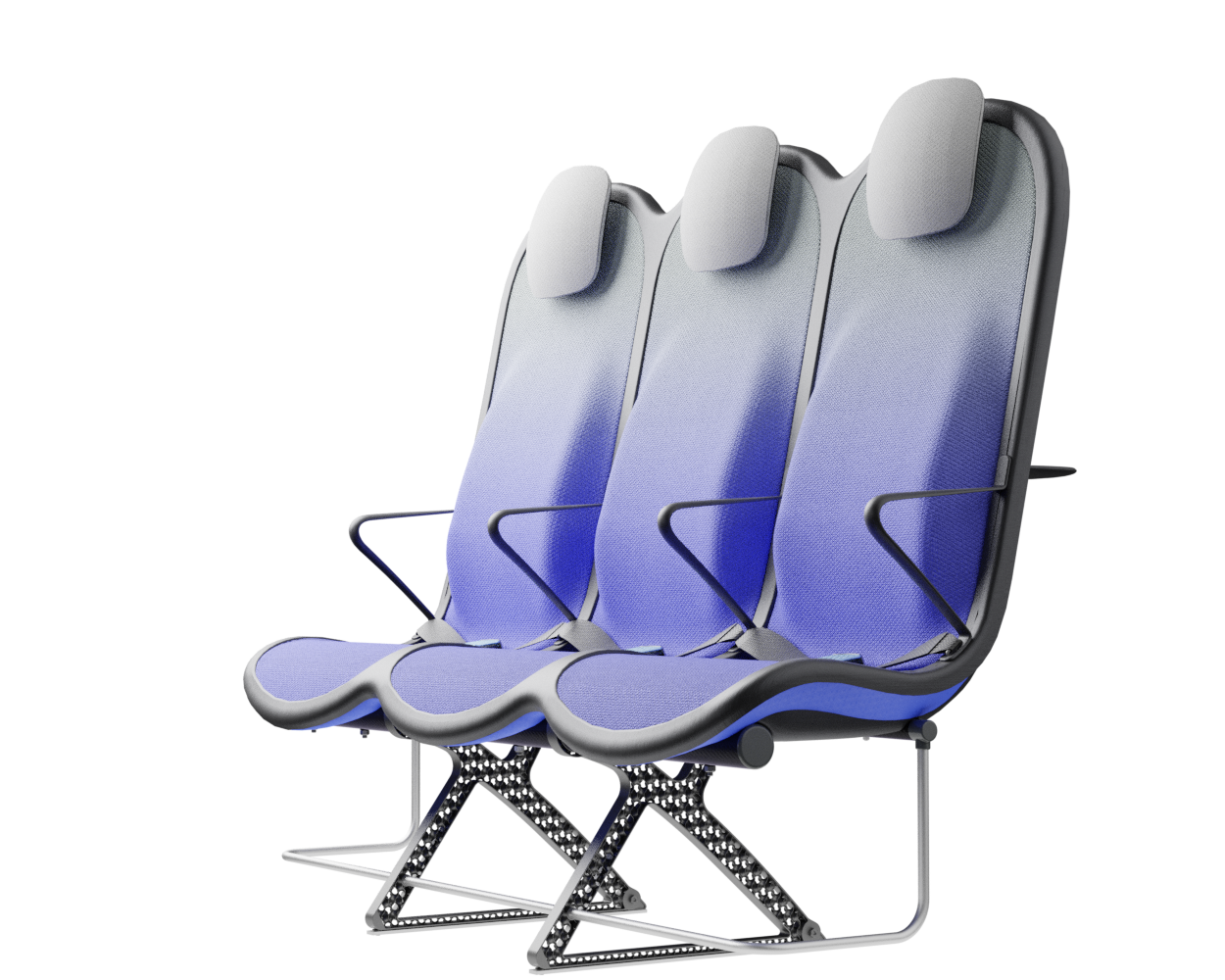
Structure
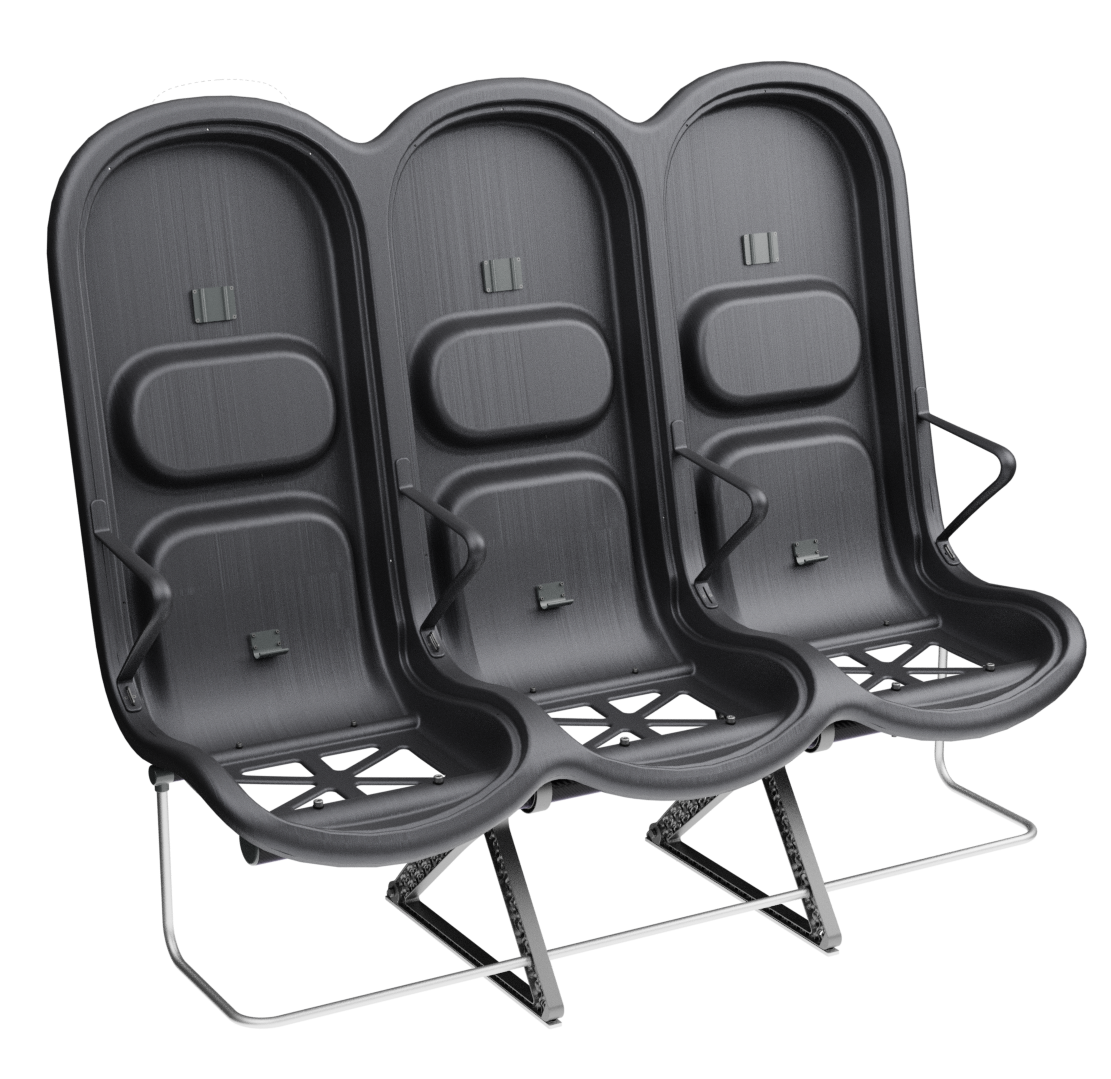

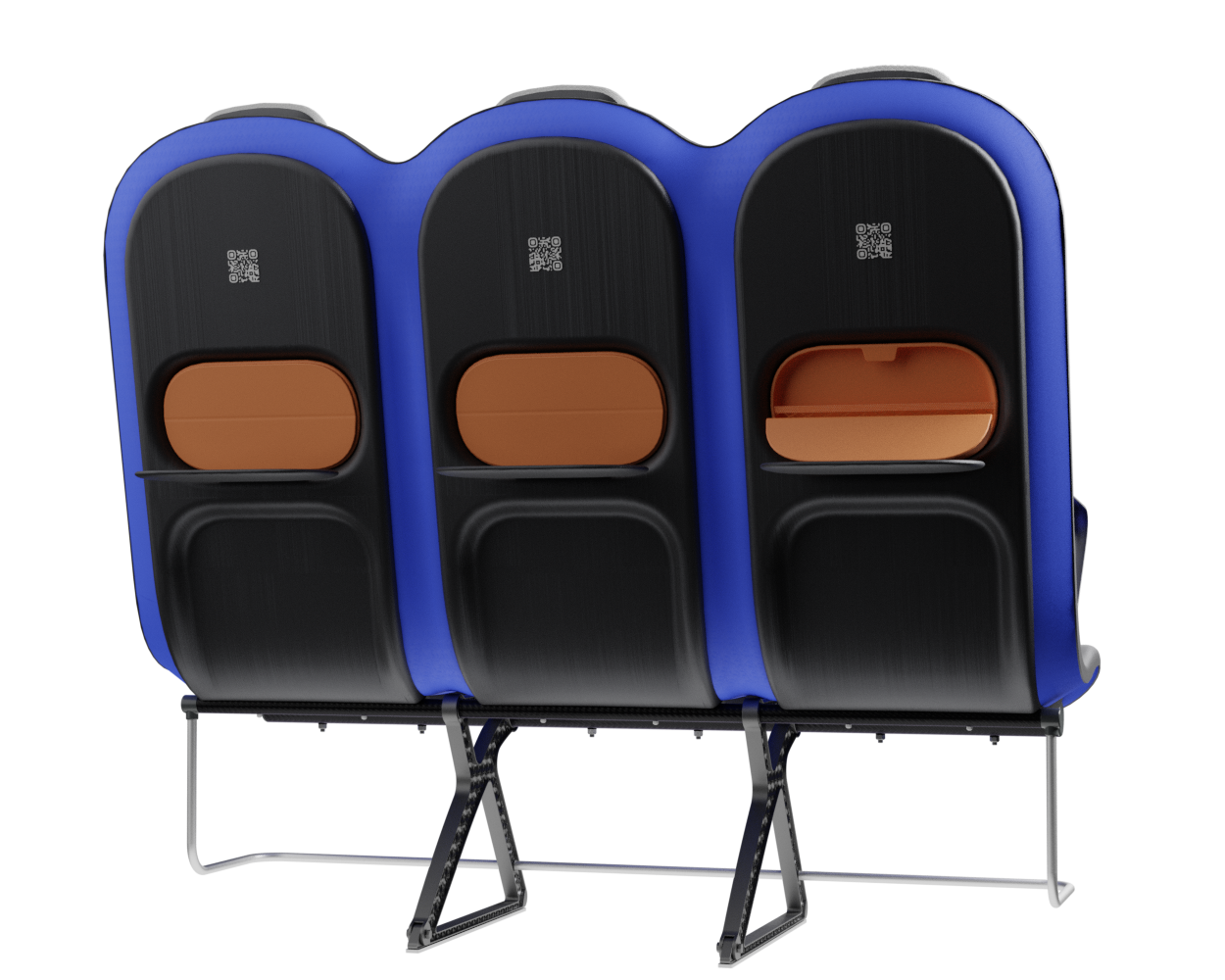
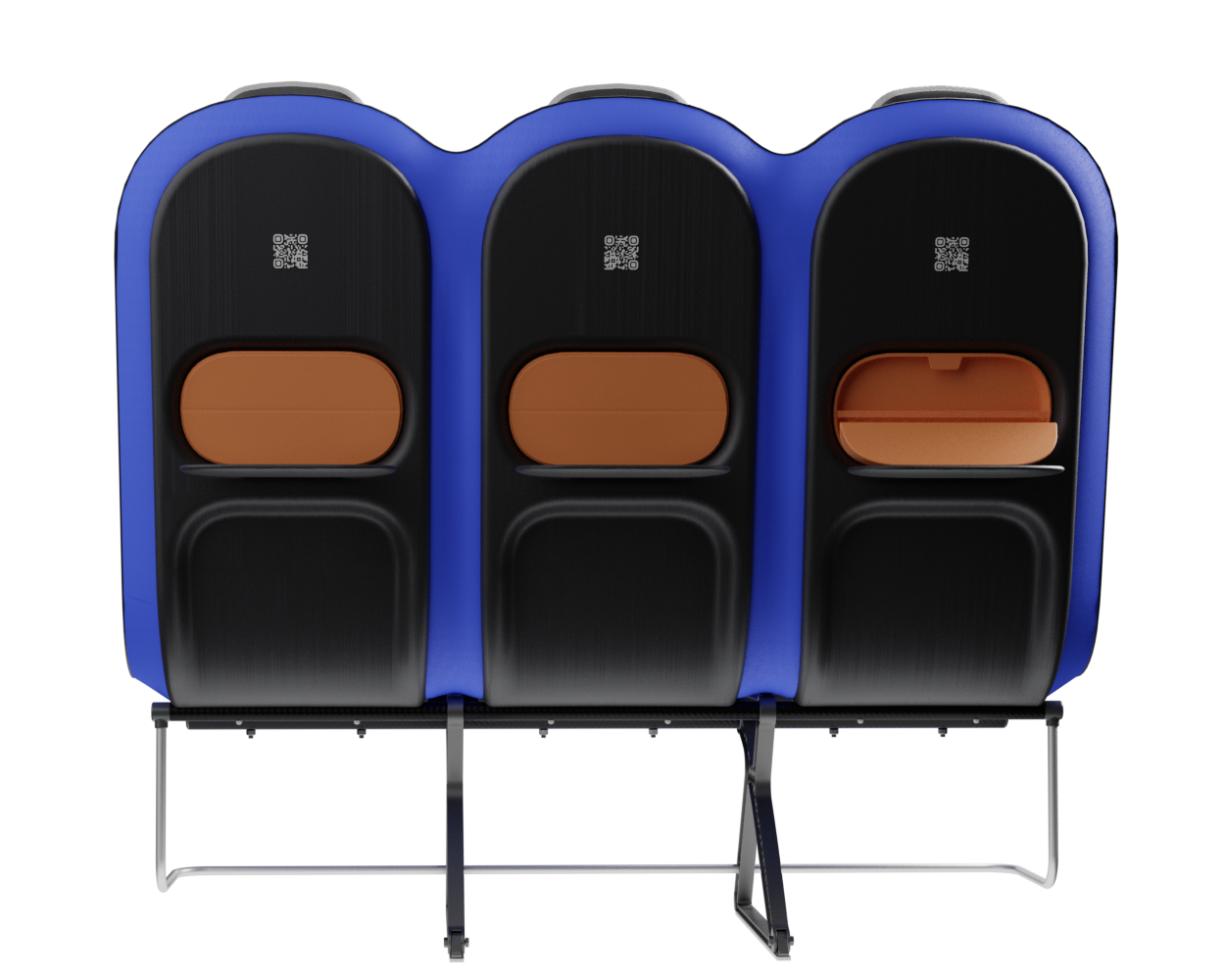
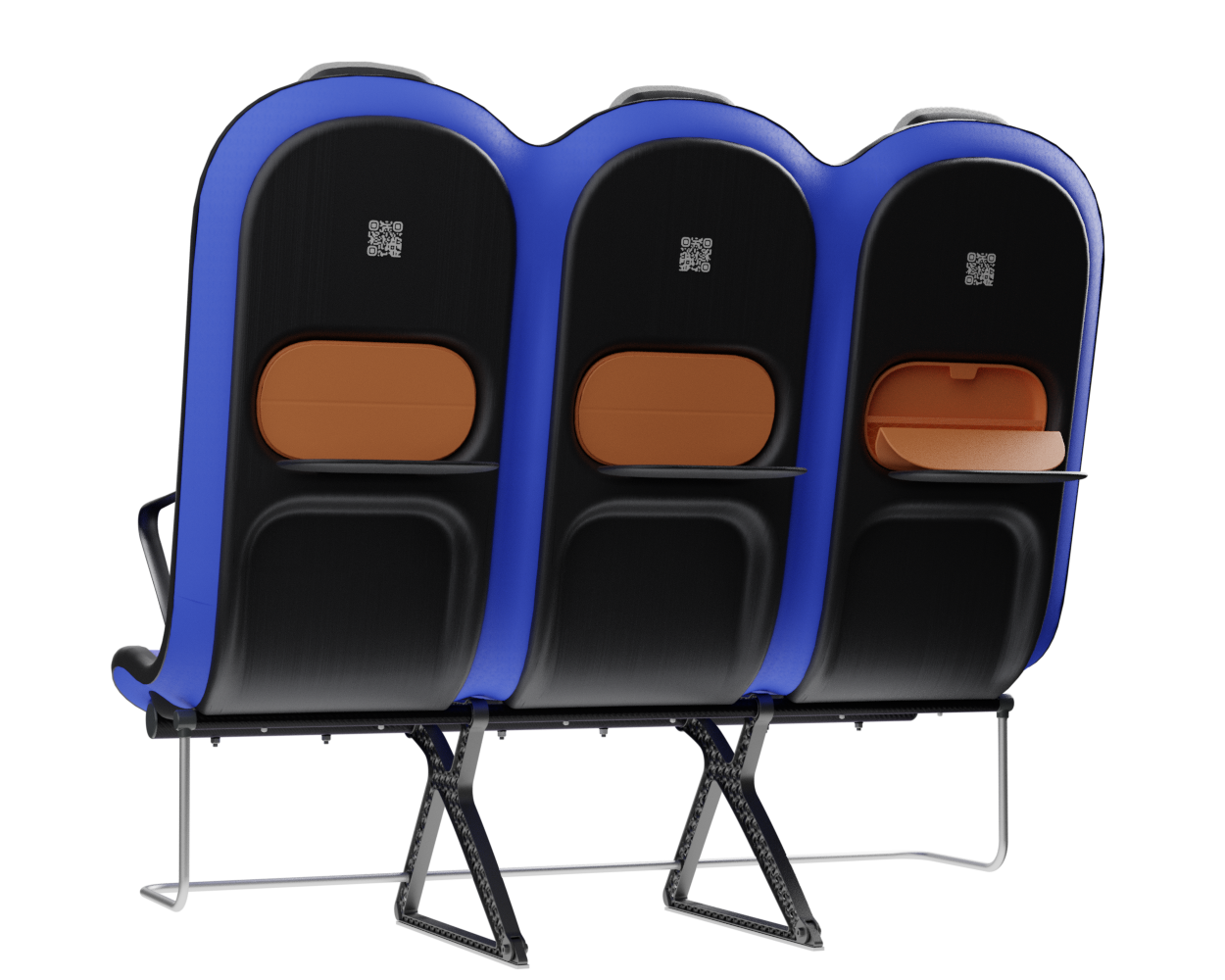
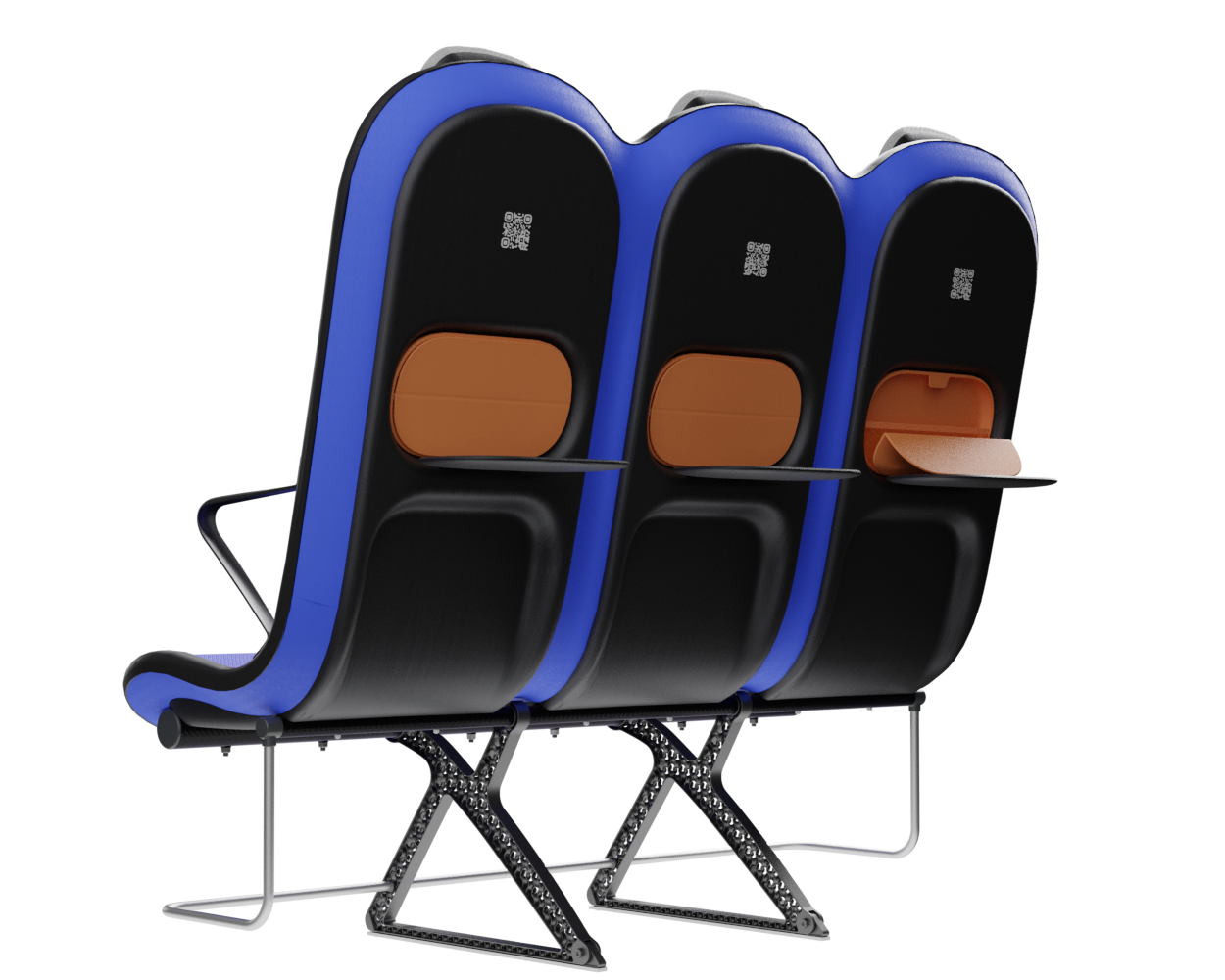
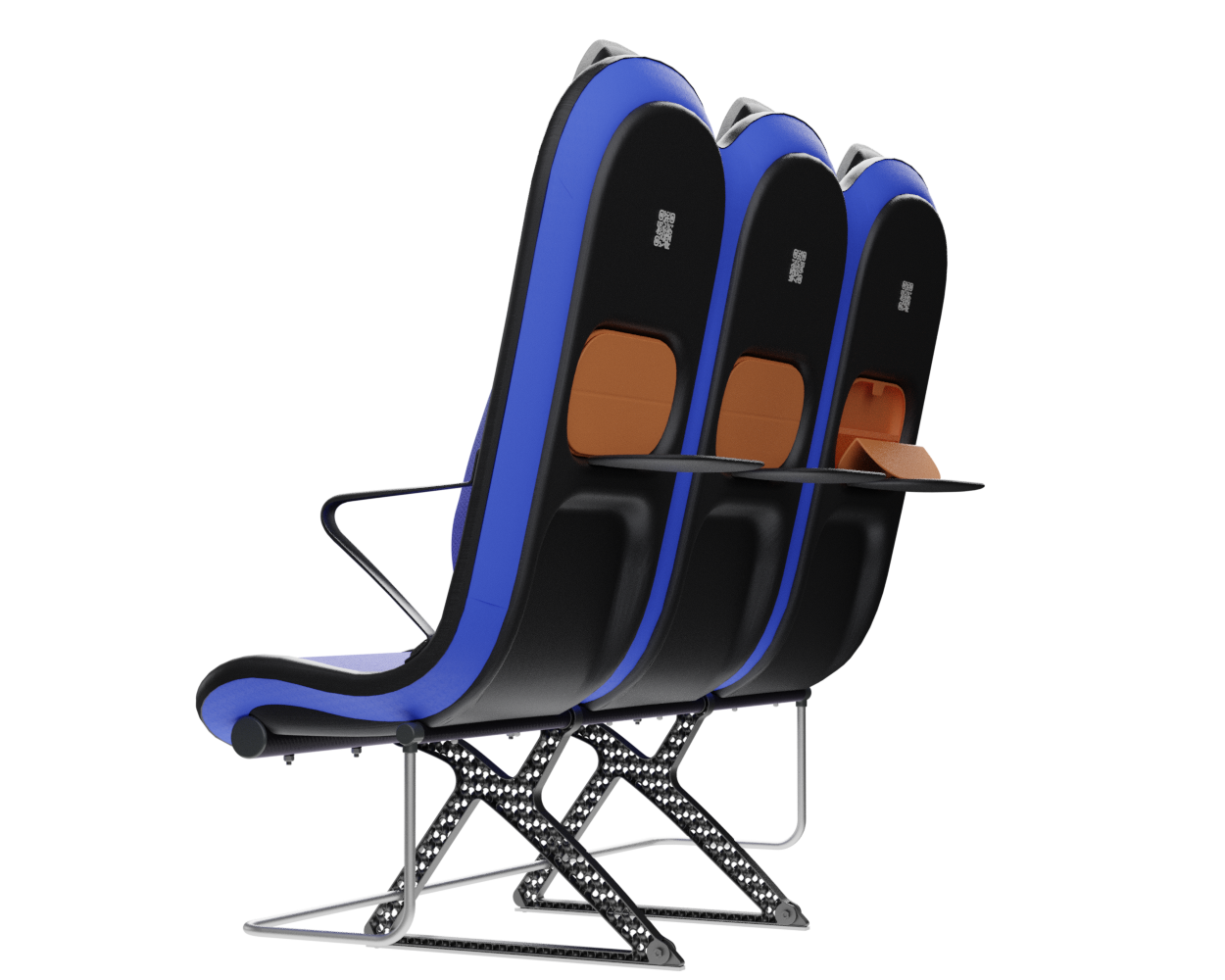
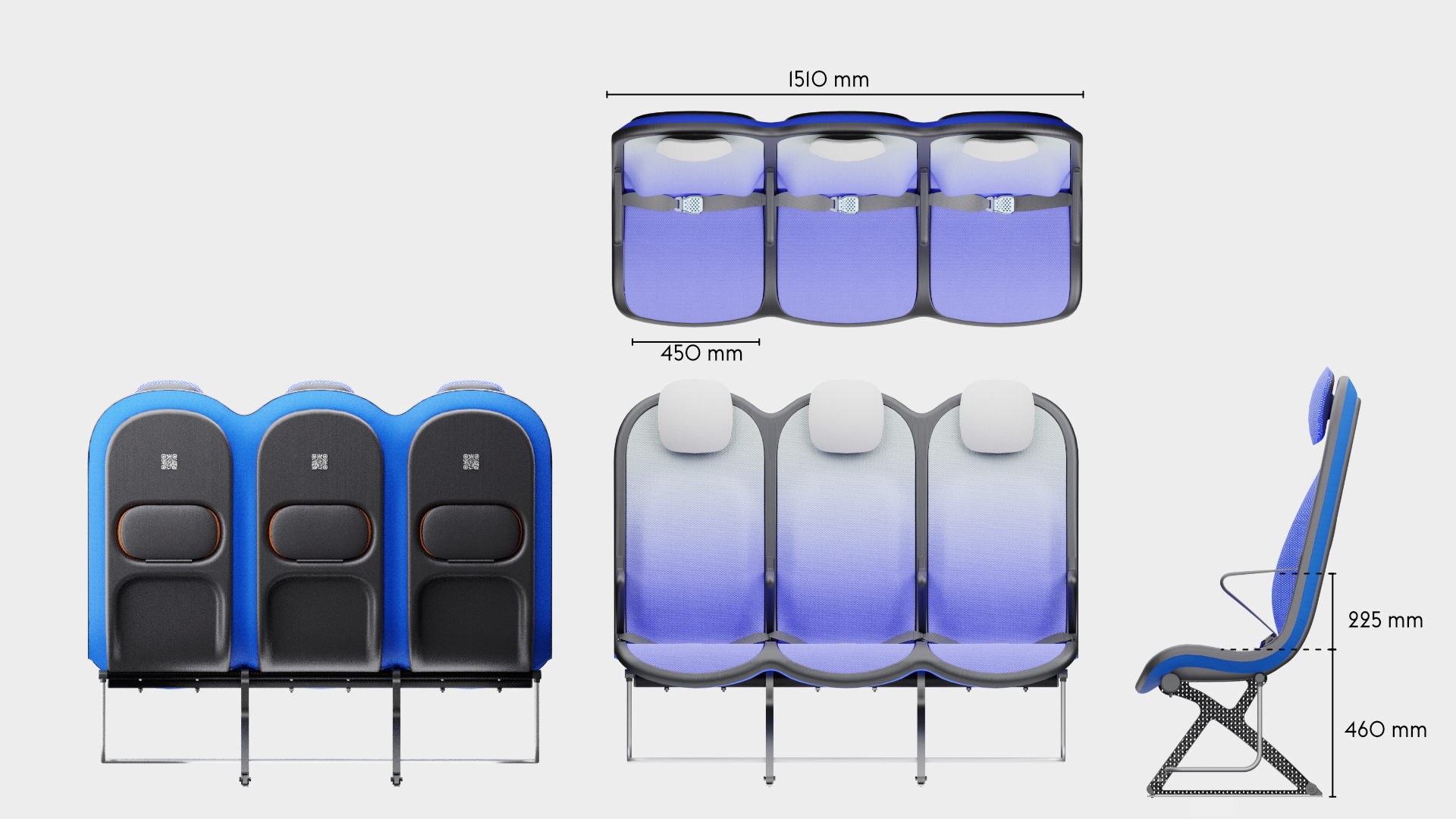
At the core of the SKY concept's structure is a rigid frame shell. The frame shell combines three seats into one bench construction, with the two outer seats now enclosing the middle seat. Consequently, the depth of the individual seat shells automatically forms a rib structure between them, replacing the structural spreaders of conventional airline seats and providing an attachment point for the armrests and seat belts. The frame is manufactured using CFRTP (Carbon Fibre Reinforced thermoplastics) compression moulding.
This material and manufacturing technique is suitable for large parts and high-volume production, making it an economical way to produce lightweight, high-performance parts.
Since the use of compression moulding creates a shell with a negative, concave side that looks unfinished, the cavities on the back of the frame are sealed with a synthetic leather covering - this leather covering gives the design a more voluminous feel. synthetic leather was chosen to provide ease in maintenance and cleaning.
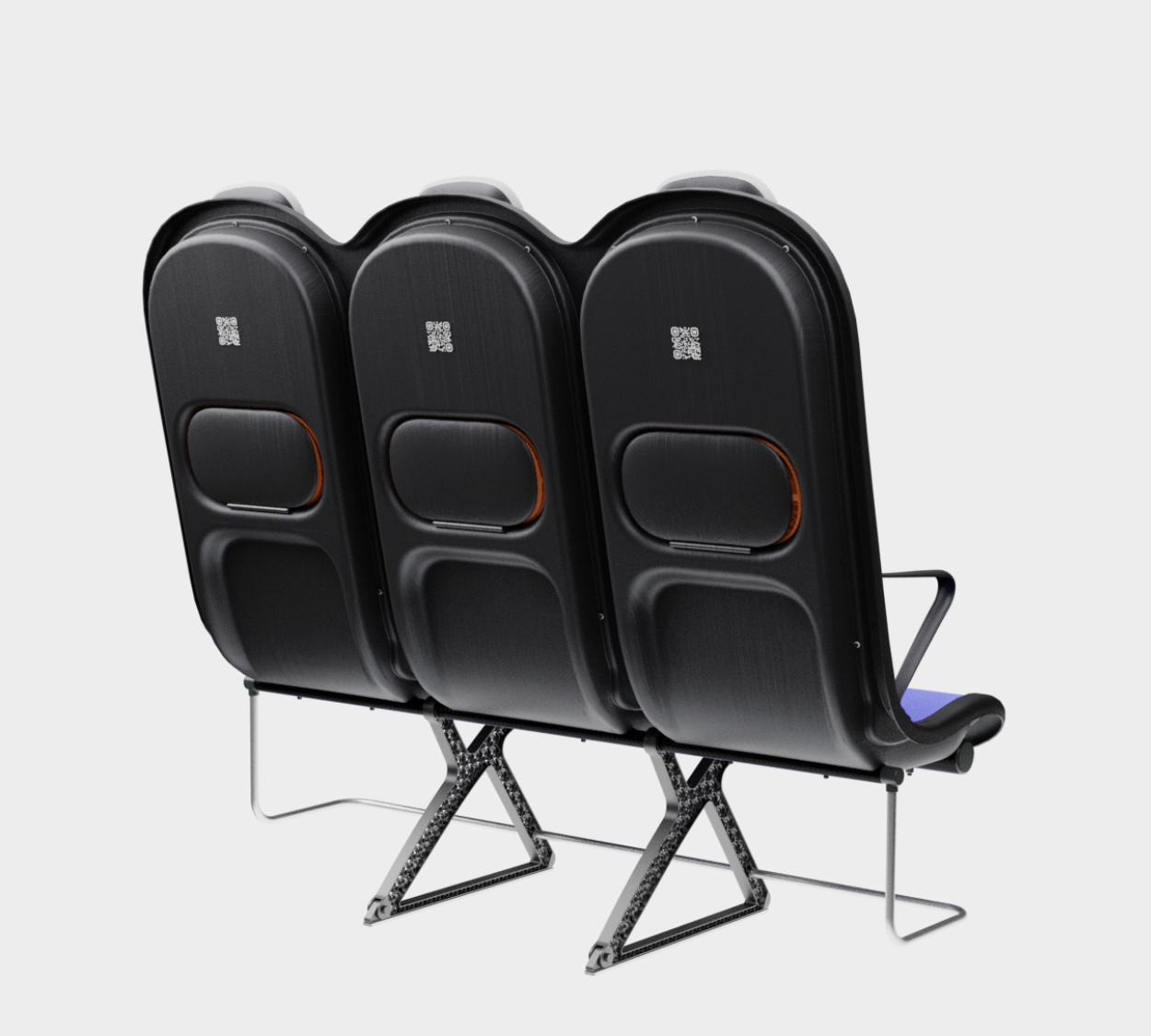
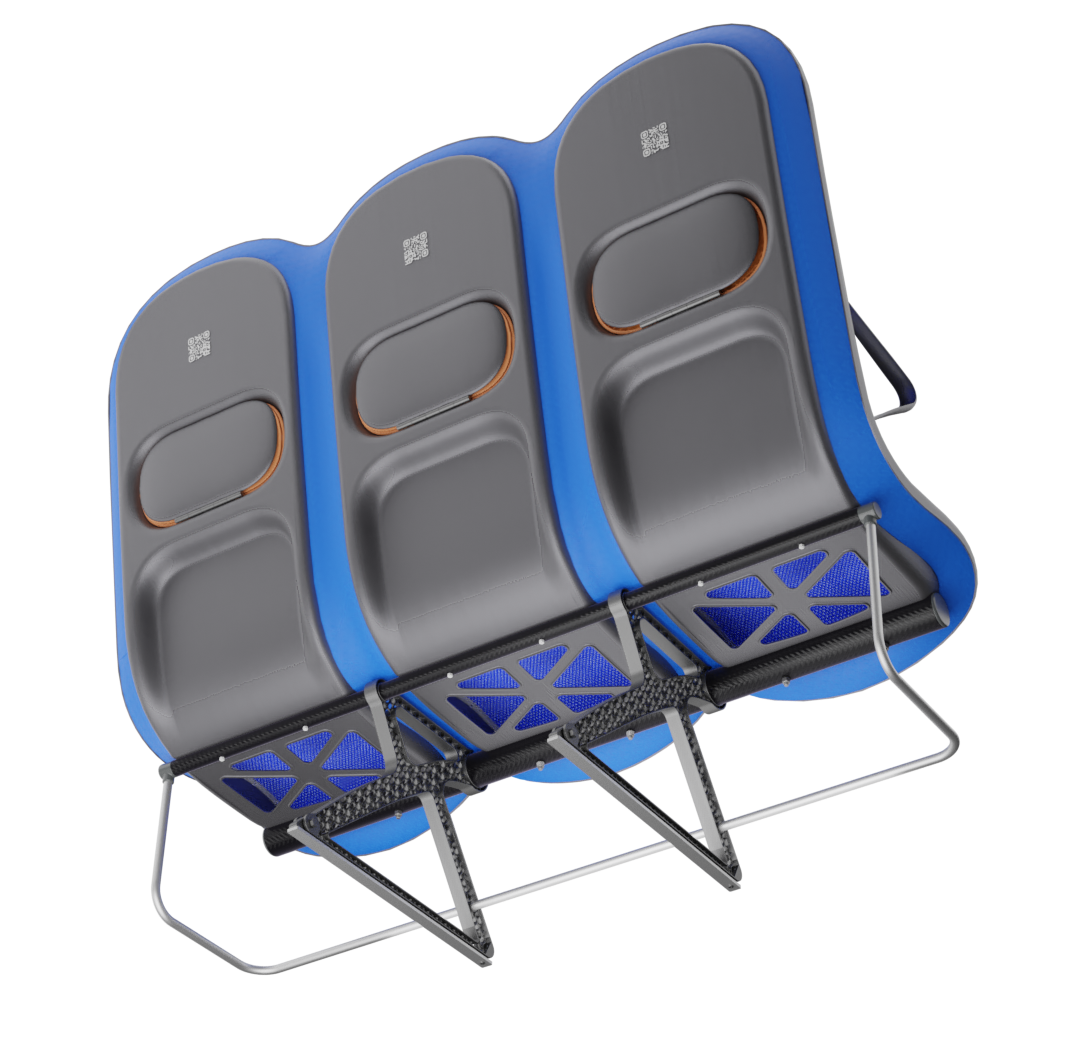



At the bottom of the frame, two CFRTP tubes are attached. The tubes provide additional torsional rigidity to the overall seat structure and are the attachment point for the legs. The use of the two tubes to connect the three seats is common in seats for economy aircraft because it allows only one pair of legs to be used under the seat, with the tubes distributing the forces of the ''shell'' to the legs. The tubes have a round profile because this profile shape is the most resistant to torsion.
Legs
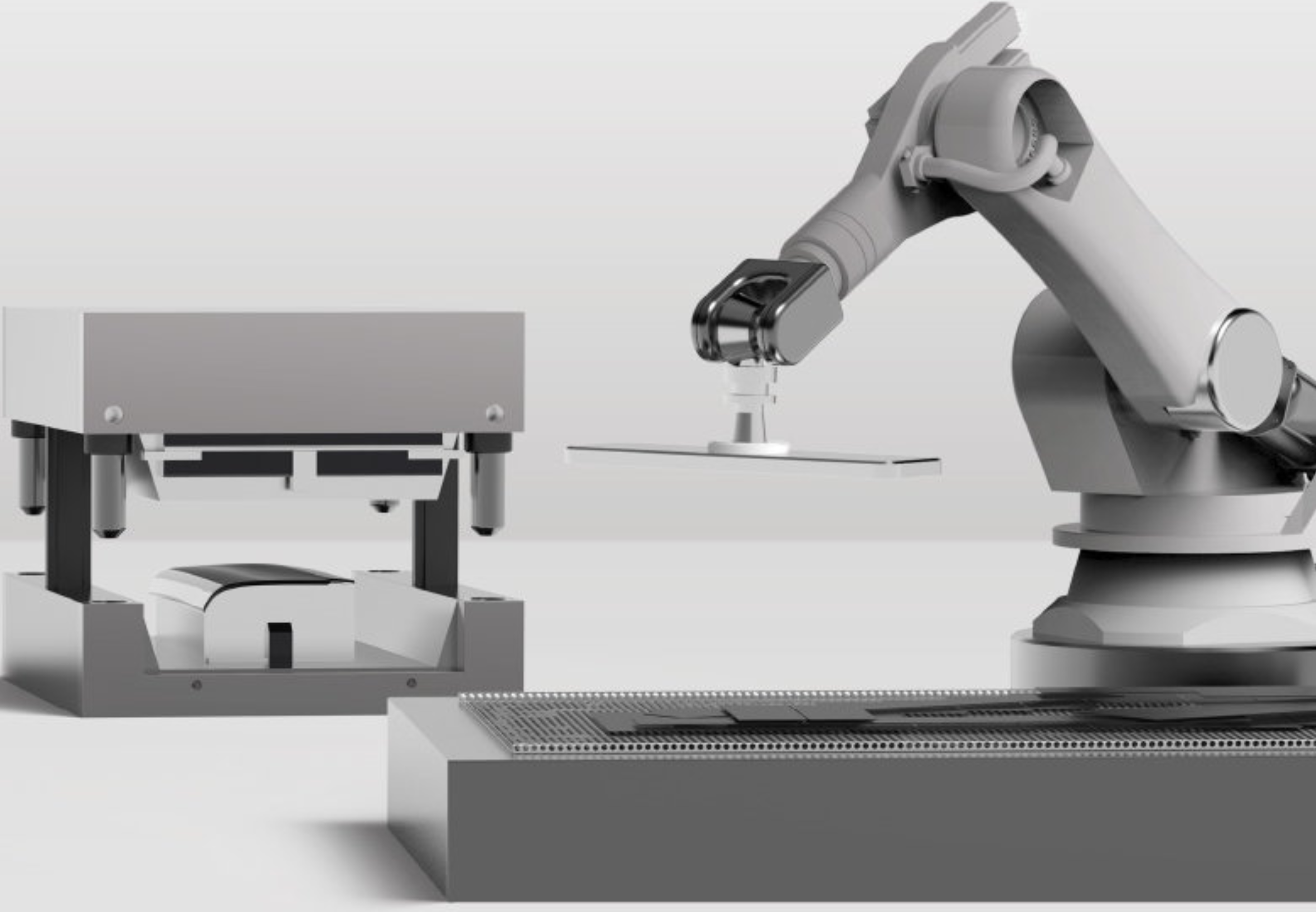
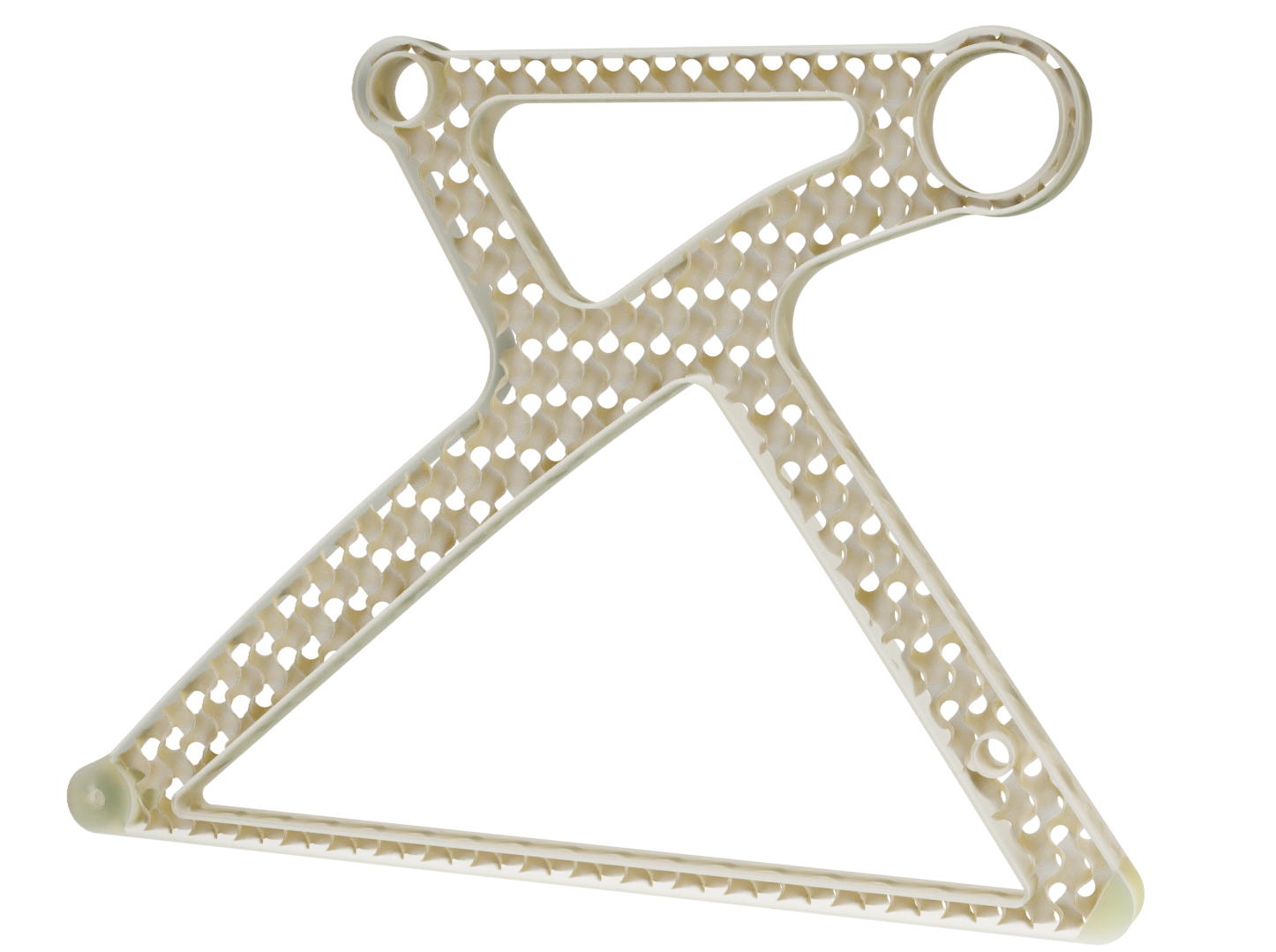
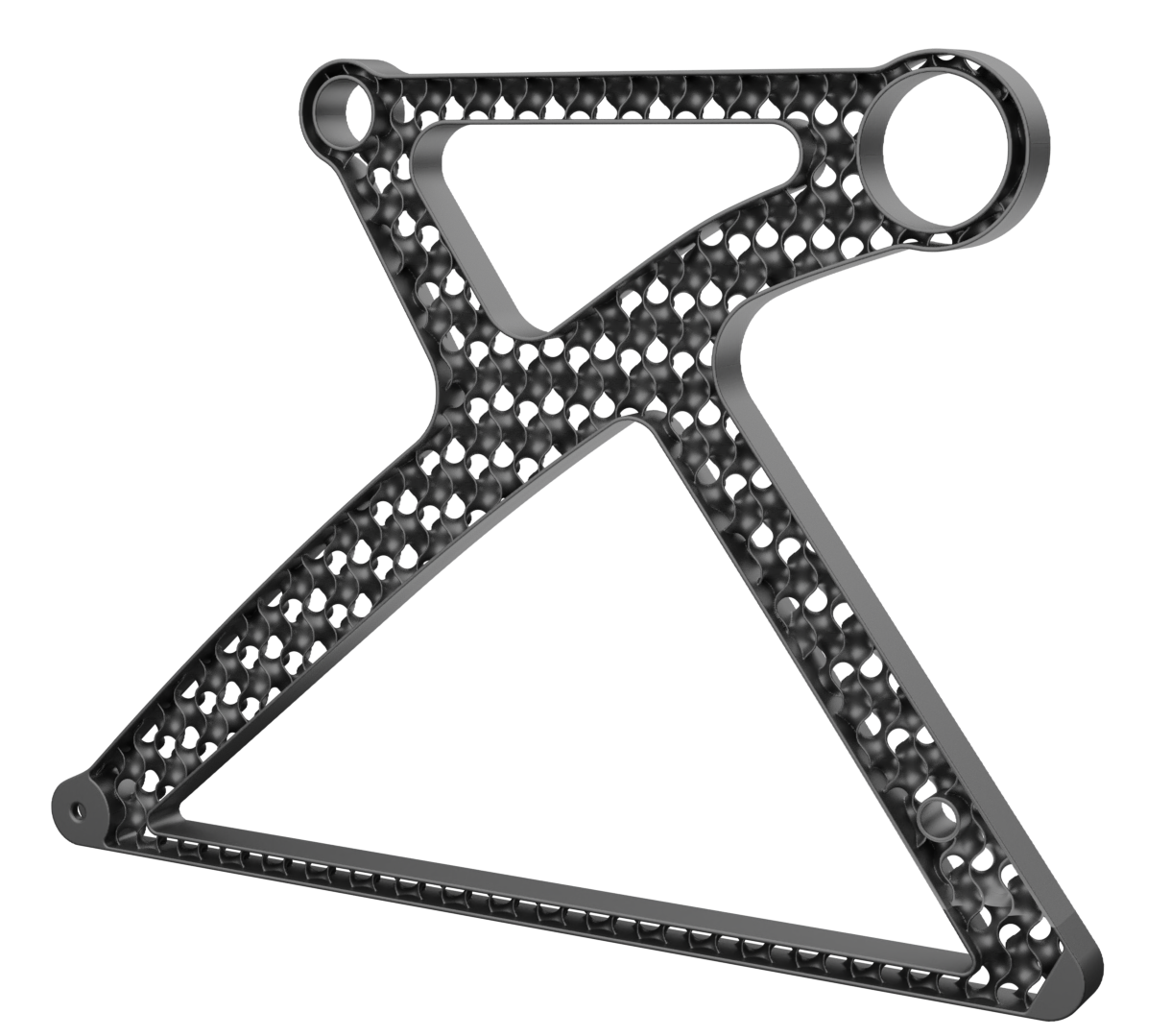
The legs are made from aluminium and have a gyroid lattice inside. The gyroid inner lattice combined with the outer ribbing creates a lightweight porous sandwich structure that can provide high strength, stiffness and good energy absorption at a reduced weight.
The seat legs will be made with investment casting as this allows to produce a complex and detailed topologically optimized metal part without using expensive metal printing.
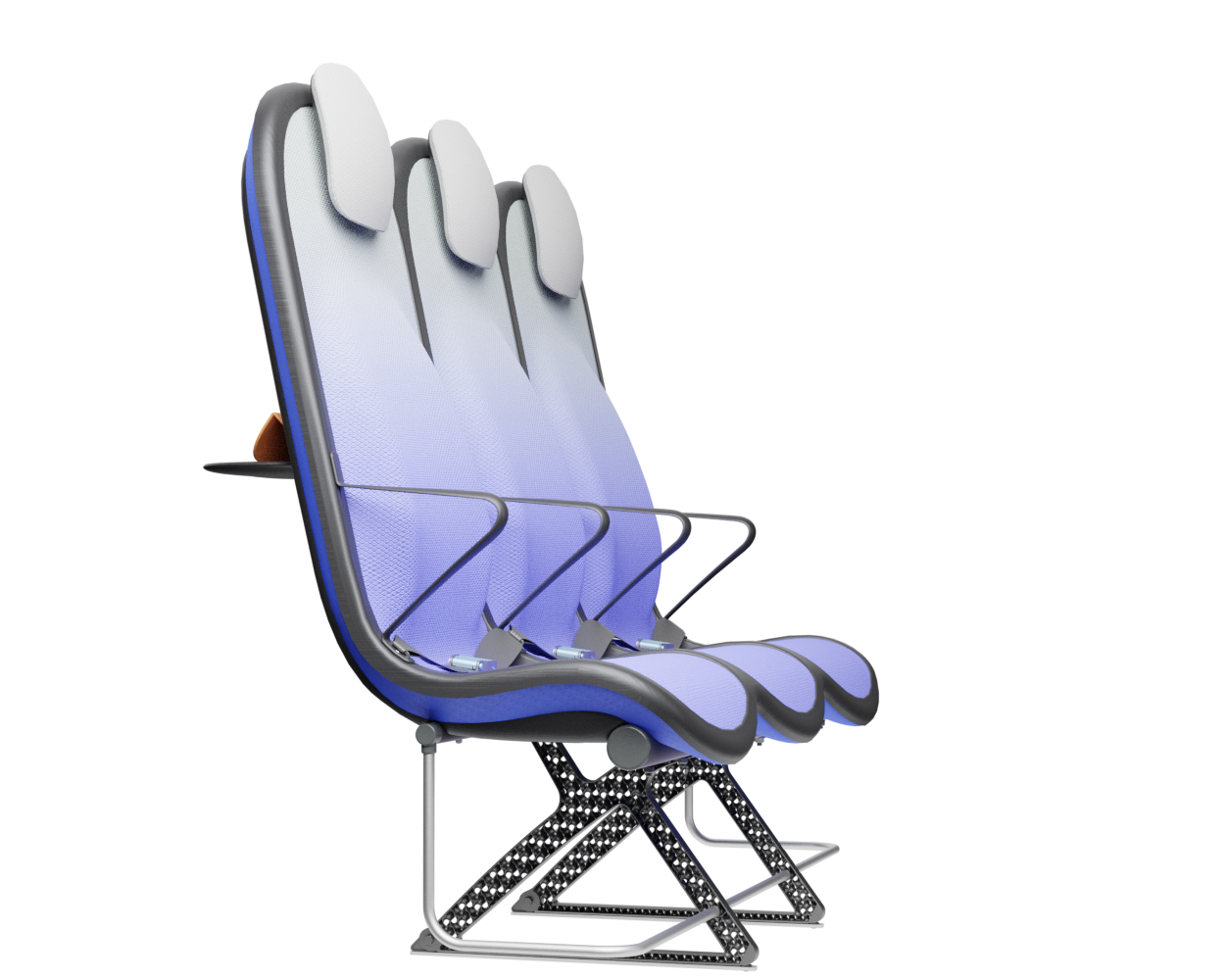
Comfort
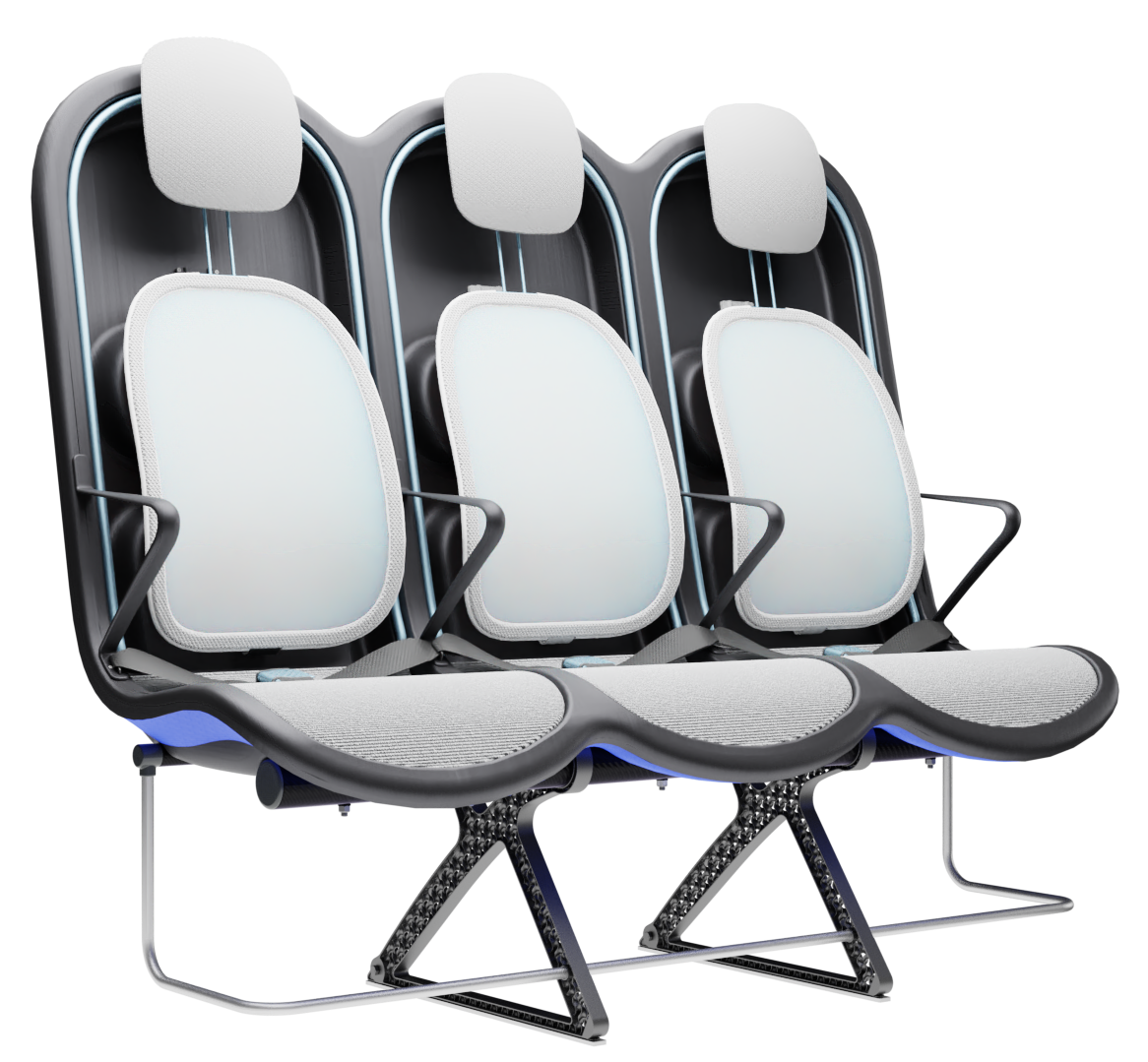

Suspension system
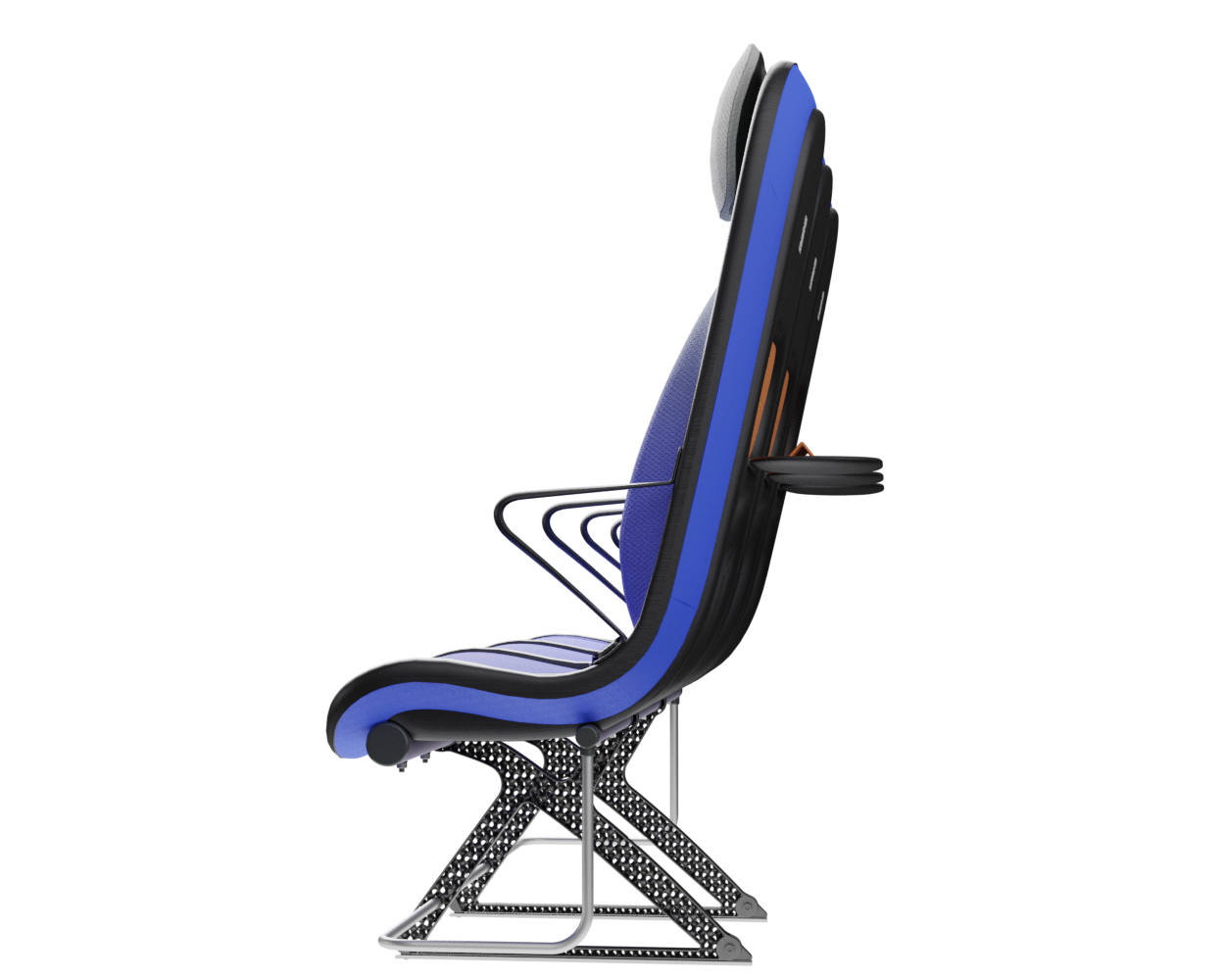
The sky suspension system substitutes the conventional and heavy foam backrest with a dynamic and lightweight back support. The springy behaviour of this suspension system supports micromovements which can alleviate discomfort over time.
The suspension system of the backrest is made from lightweight bent spring-steel rods, to which a pre-tensioned suspension fabric is attached. A lightweight, easy to detach aluminium frame is used for the whole system including the backrest, the seat suspension and the headrest. The headrest uses conventional foam and is attached to a lightweight shell made from the same CFRTP material as the frame.
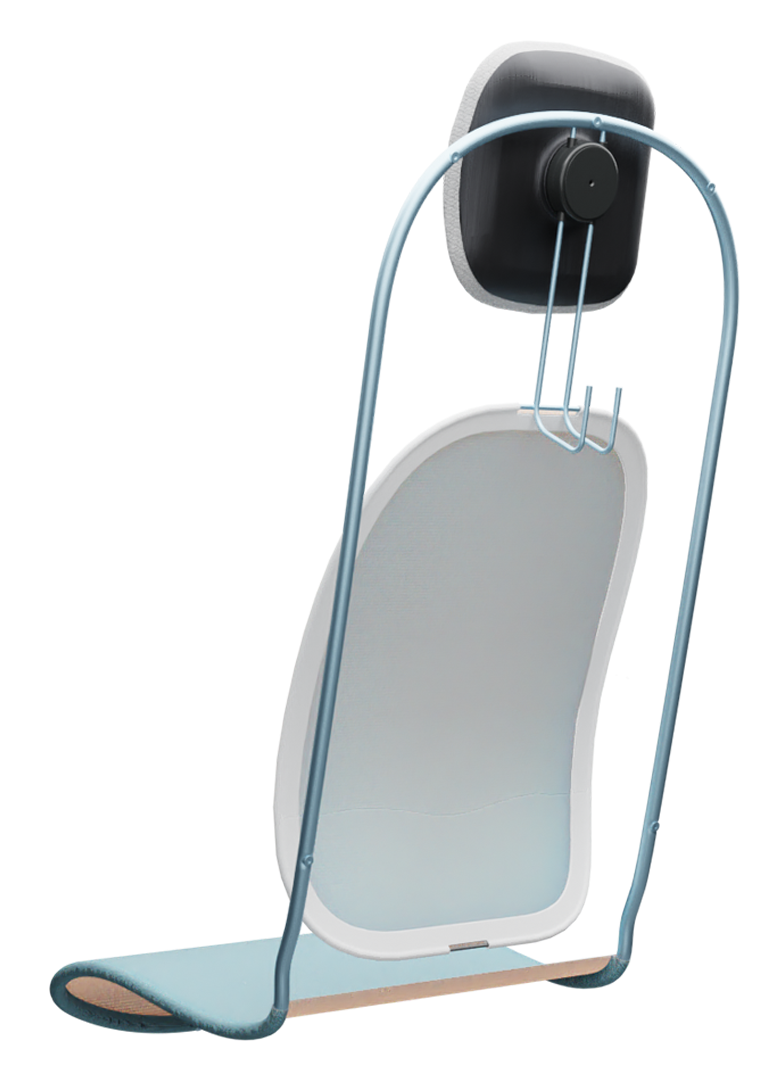
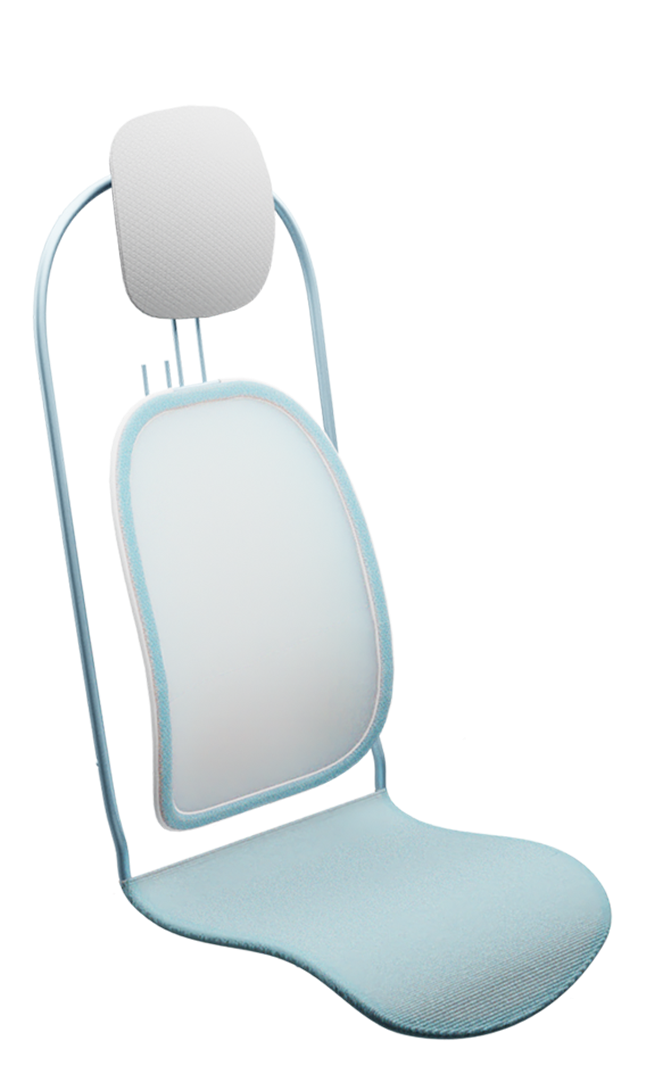


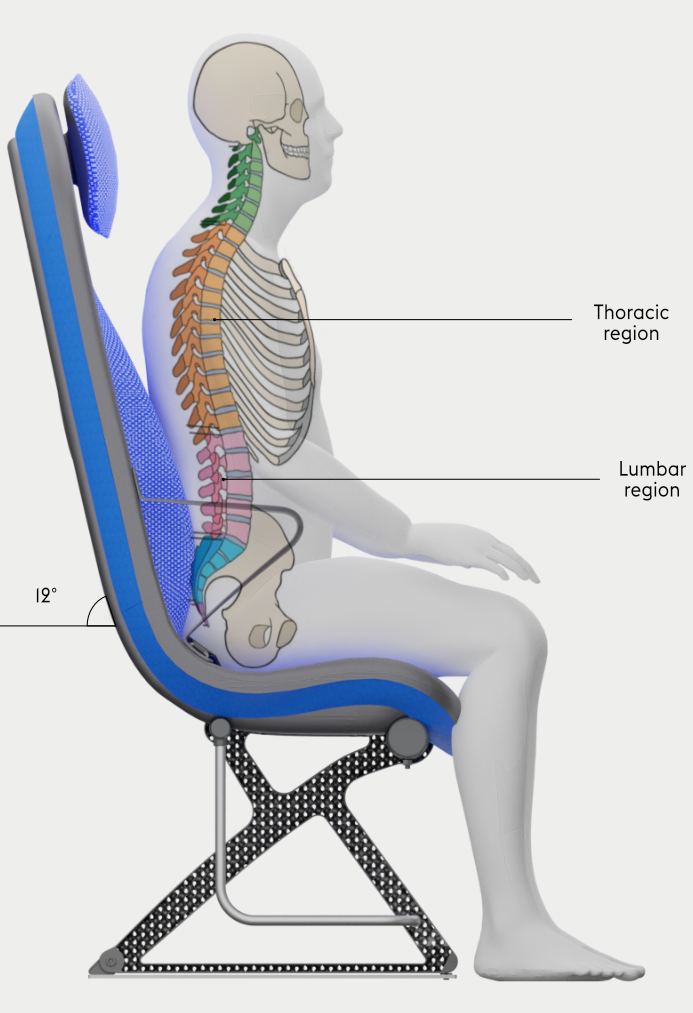
Dynamic support
Most current economy seats for short-haul flights have a fixed backrest to save weight and reduce seat pitch. However, having a fixed backrest limits the freedom for variation in posture.
The more dynamic suspension system of the sky concept supports the back in the lumbar and thoracic spine area, while the springy behaviour of this suspension system supports micro-movements that still allow for slight variations in body posture.
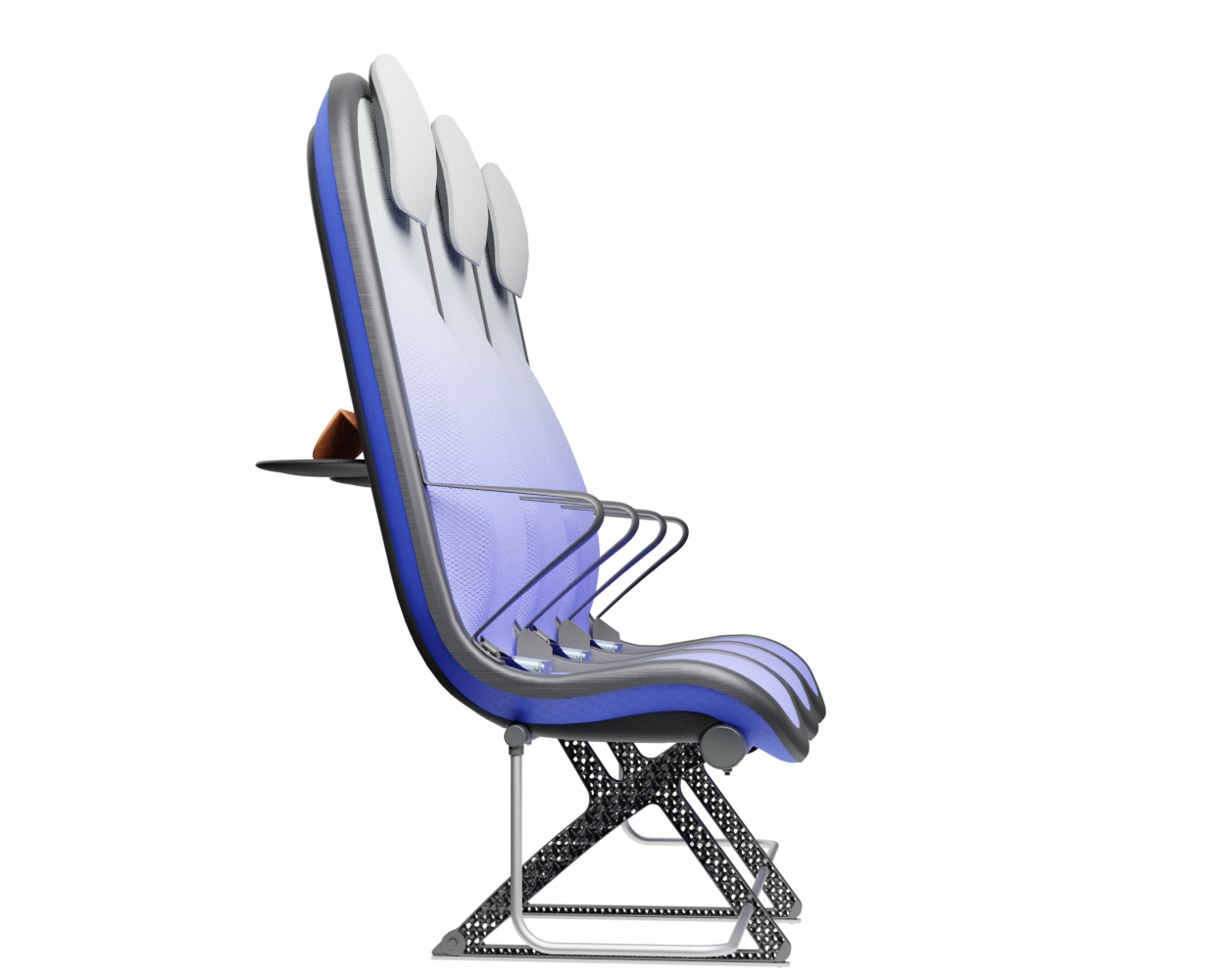
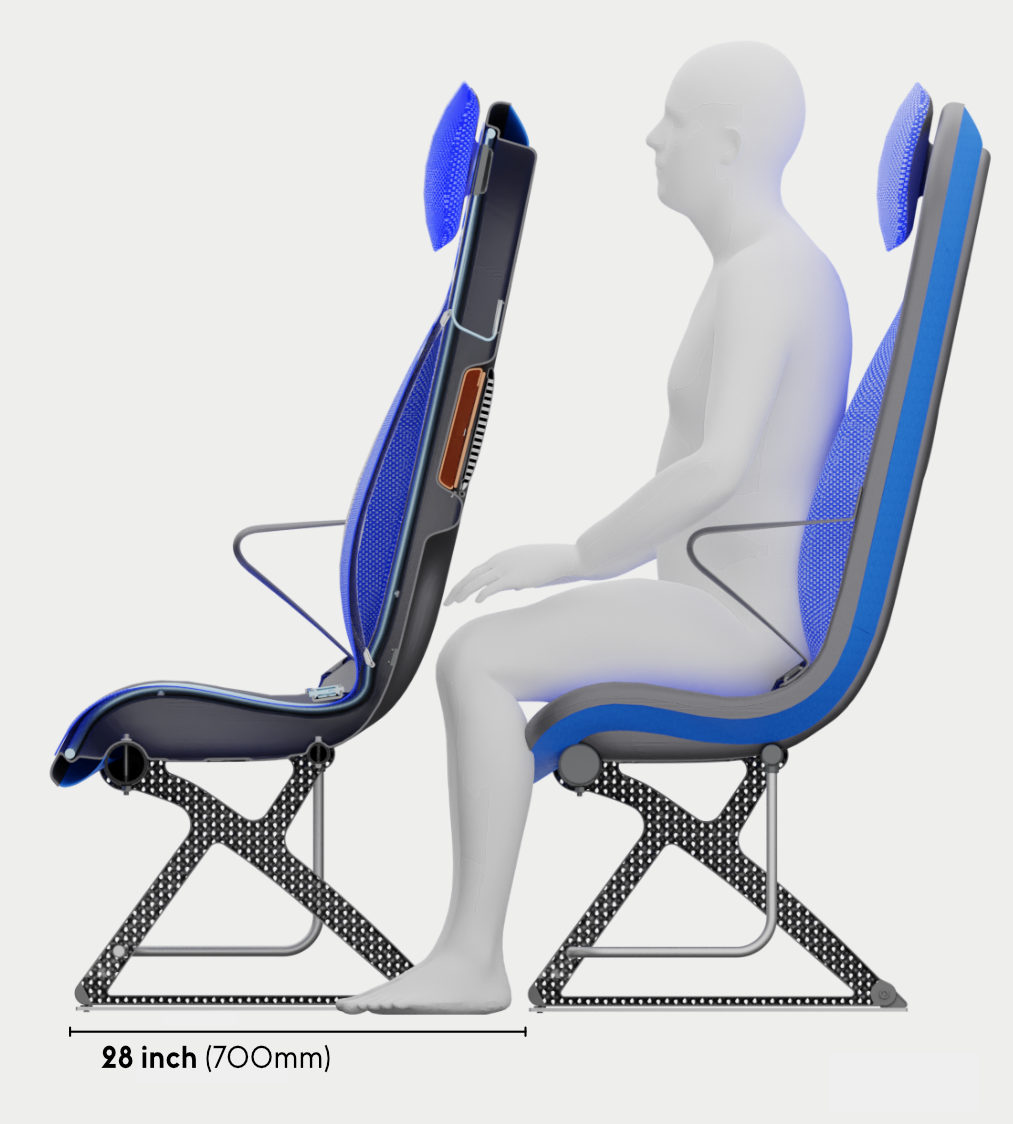
Knee cavity
The cavity in the back of the frame shell creates 50mm extra space around the knees. Allowing for an efficient pitch spacing of 28 inches.
Details
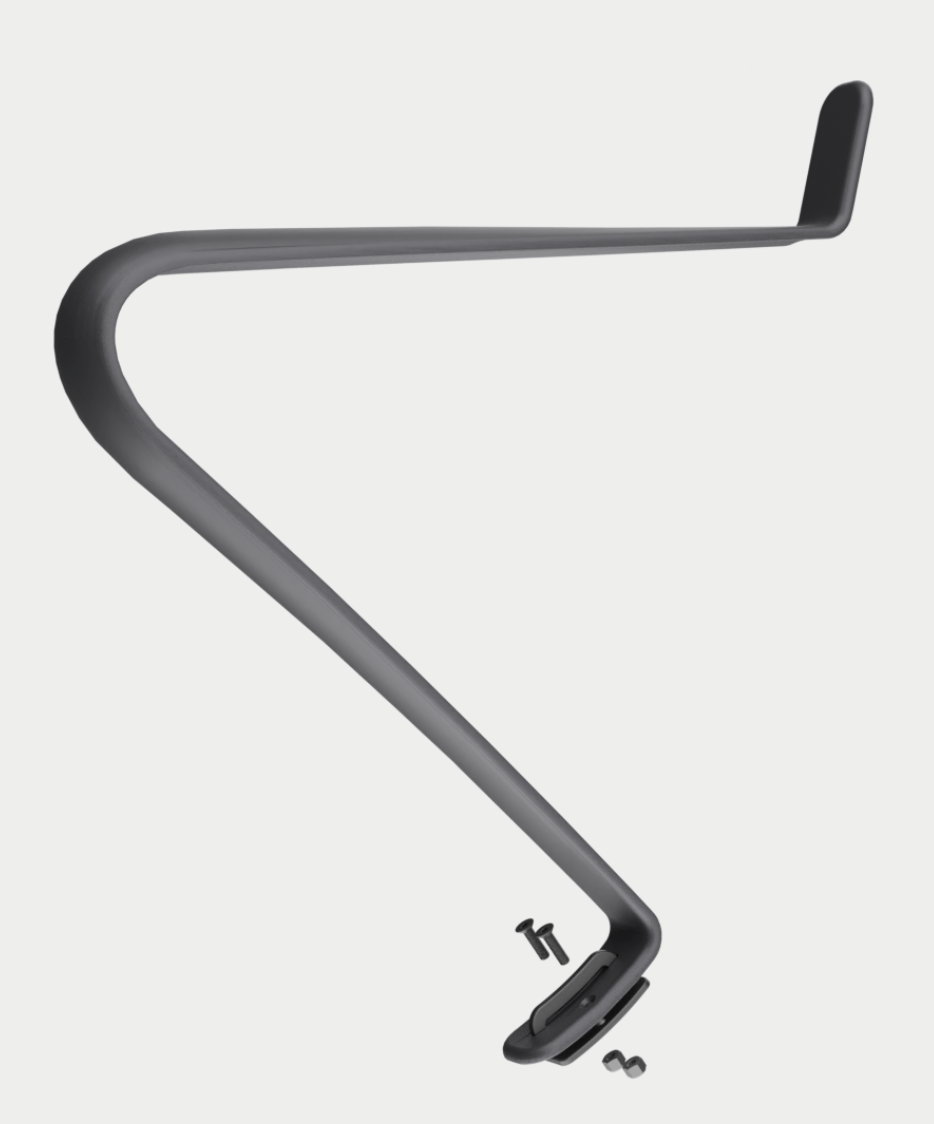
Armrest
The armrest is also made with compression moulded CFRTP, while its curved profile adds flexural rigidity making for an ultralightweight mass of only 70 grams.
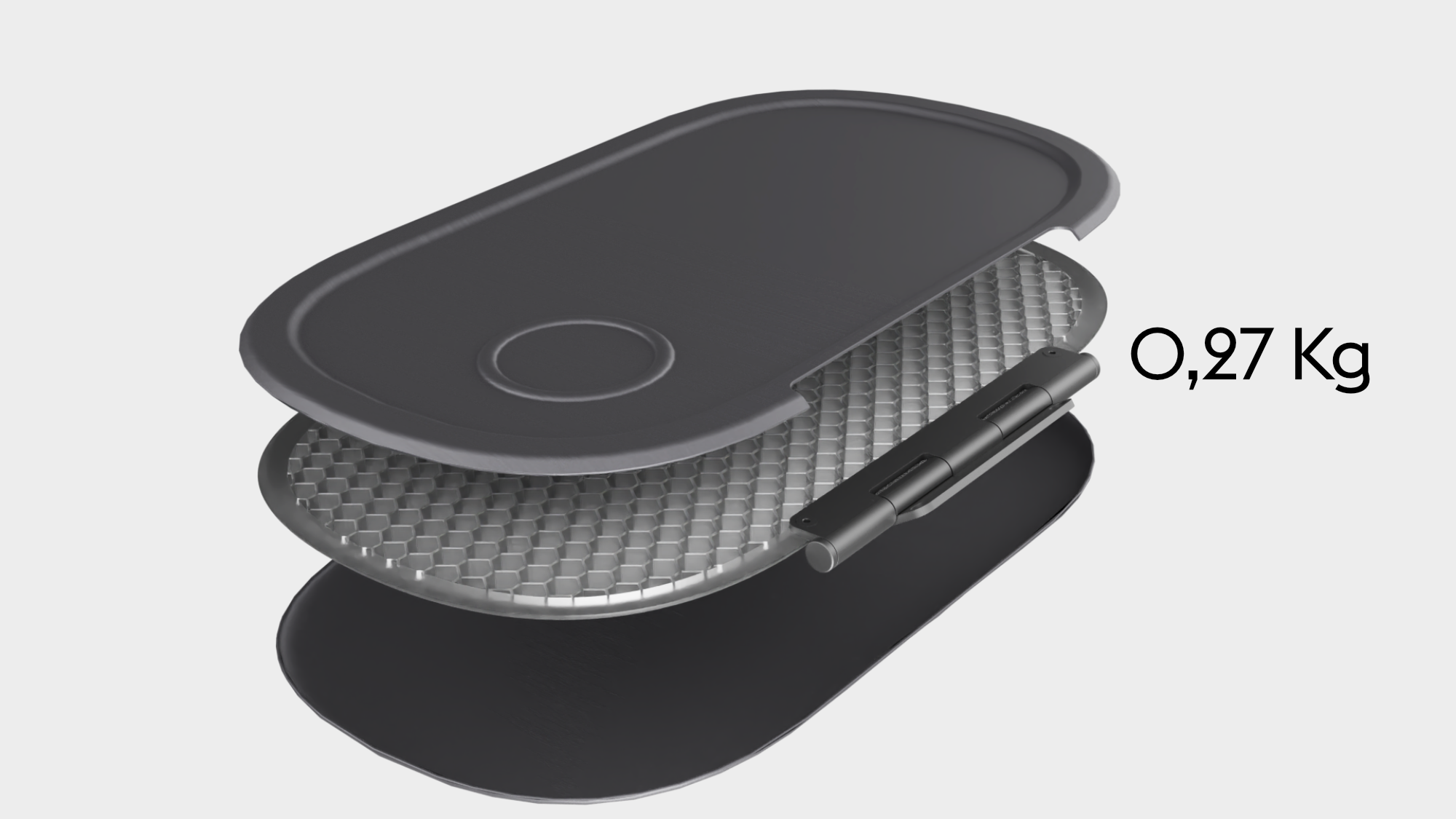


Tray table
The tray table is also made of the CFRTP Maezio. The tray table consists of two thermoformed shells welded together with a honeycomb sandwich structure of polycarbonate on the inside, which is the same material as CFRTP matrix resin, so it does not affect recyclability but ensures additional necessary rigidity.
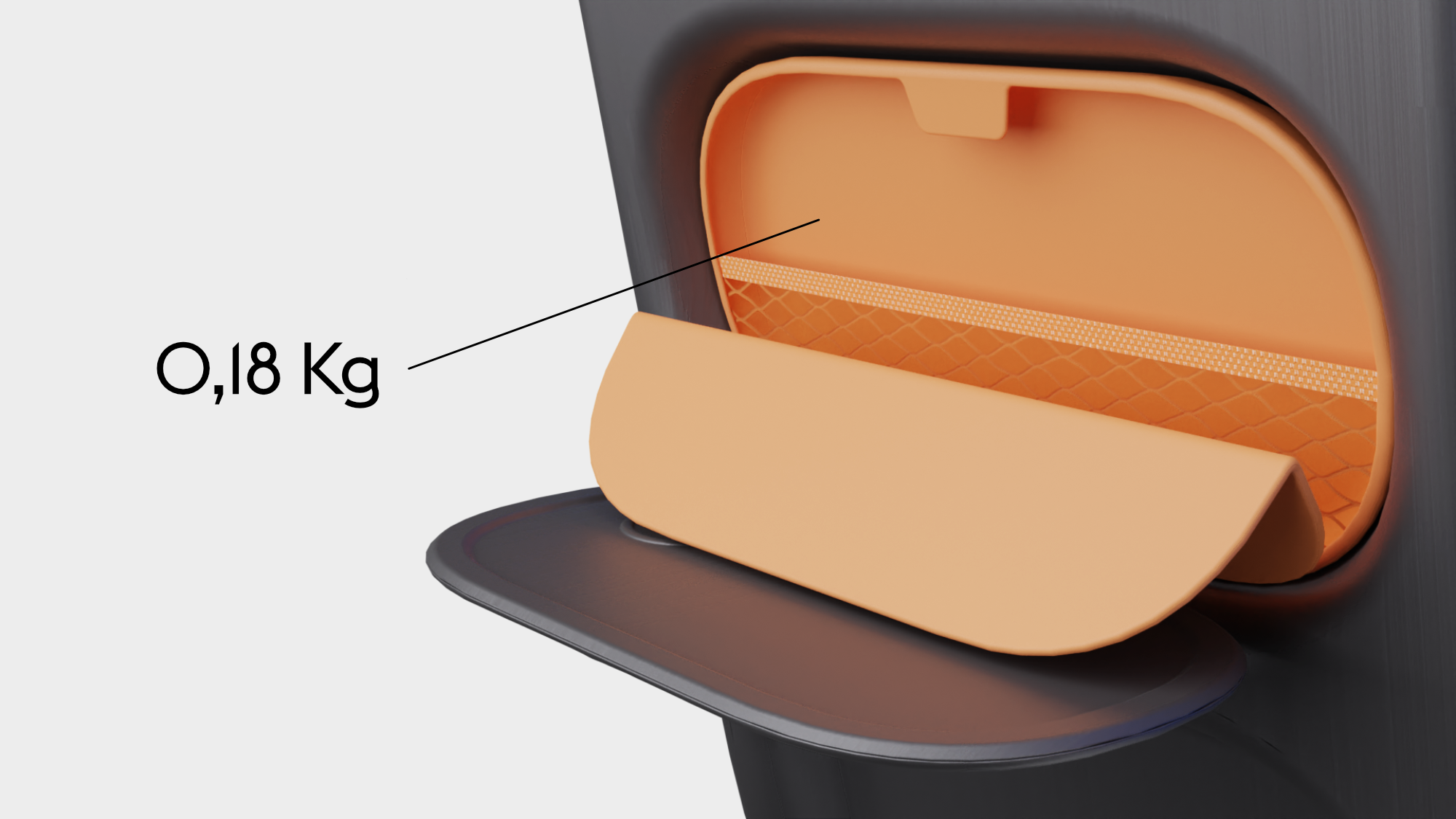
BYOD & nesting support:
To further enhance the seating experience, the seat is equipped with some features to support the nesting and BYOD trend. There is a tray table integrated into the cavity of the backrest. Behind this cavity is room to store a bag for personal items and flight information, such as safety instructions. the lid of this bag closes magnetically and can be folded into an angle so that the passenger can position their phone against it.
Test & validate
Ergonomic prototype
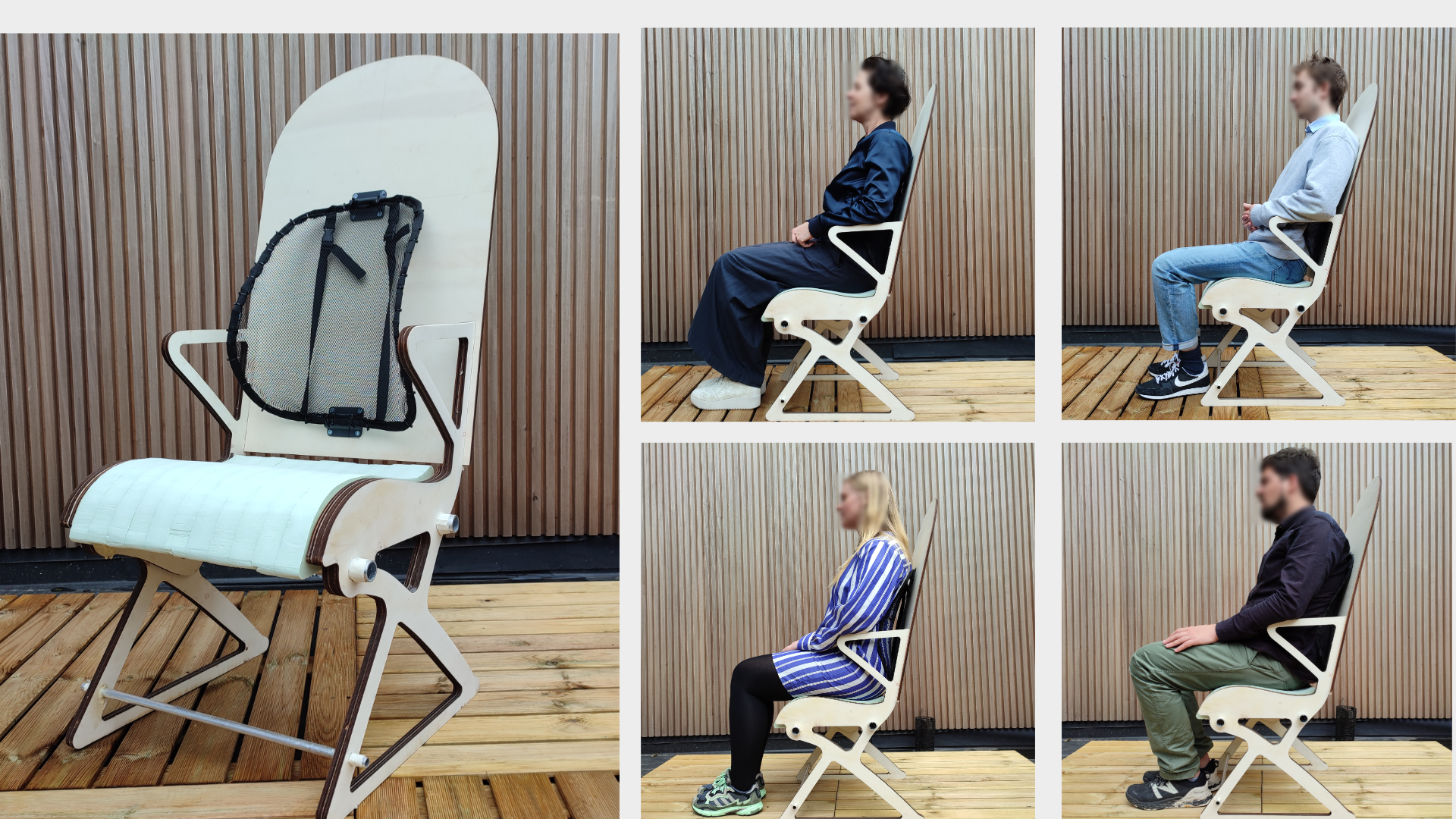


A simplified ergonomic model was made to evaluate the main dimensions and suspension backrest position, size, and overall feel. A lightweight spring steel frame was made as a prototype of this suspension system, and a net was stretched over it as a replacement for the Dynaflex suspension fabric. The main concept attribute to evaluate with this mockup was if the seat-back suspension could be a valid alternative to the replacement for foam backrests of conventional airline seats. Five adults with different heights and body sizes tested the model; Their feedback provided valuable insight on the sitting experience of the concept in its current state.
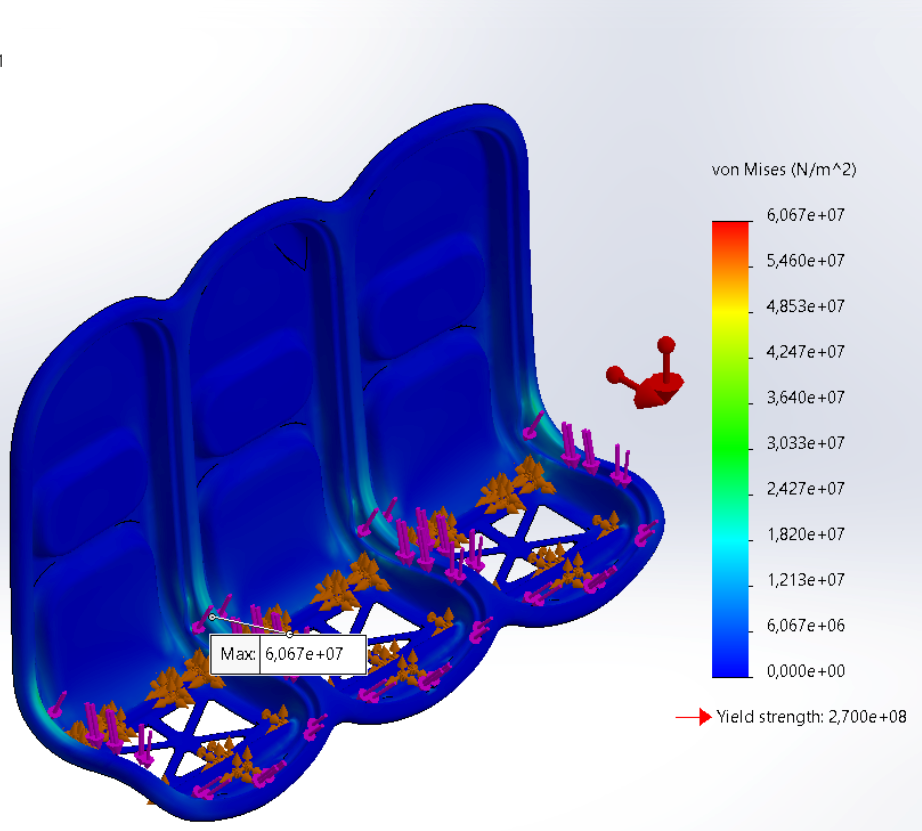
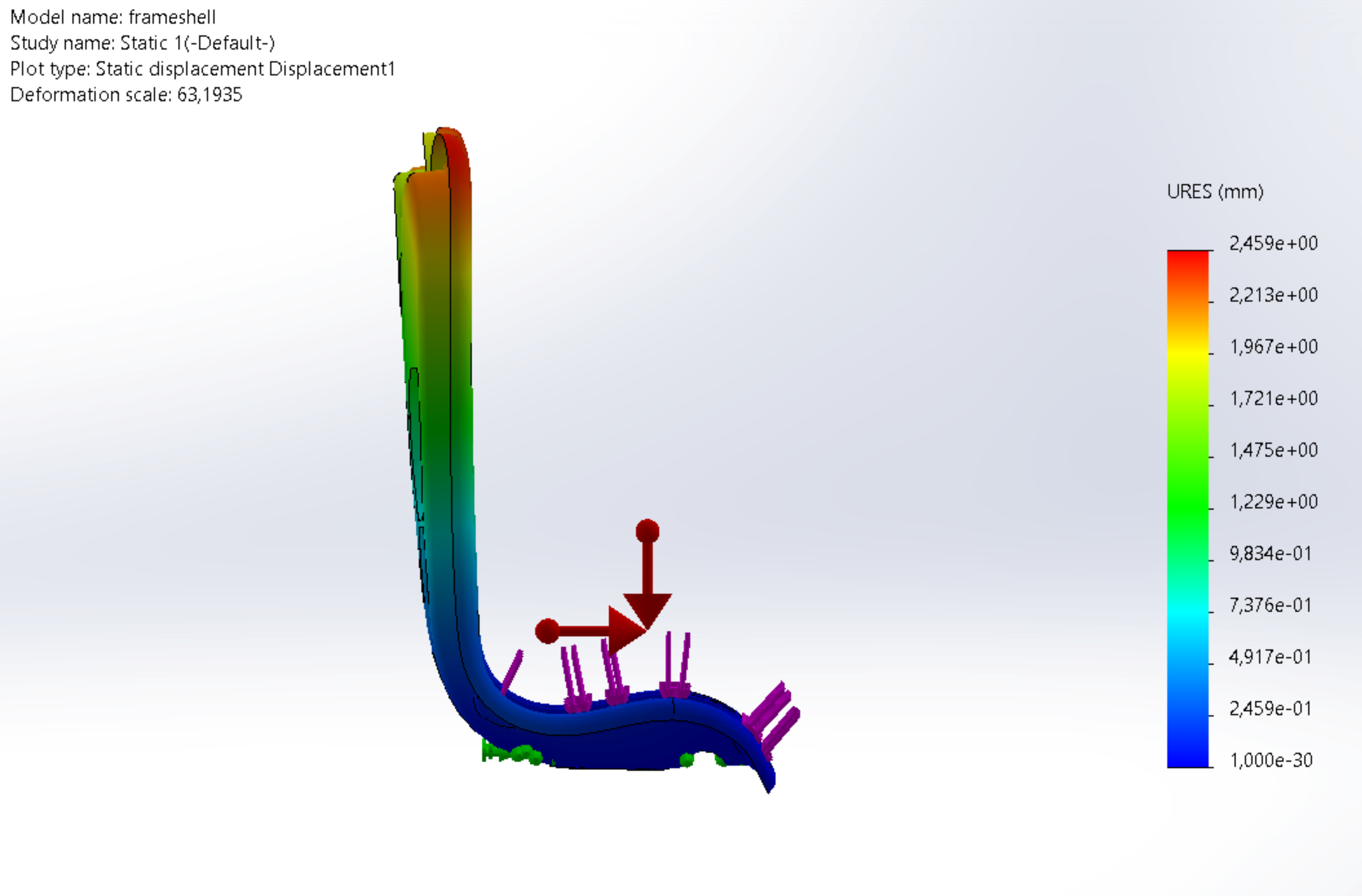
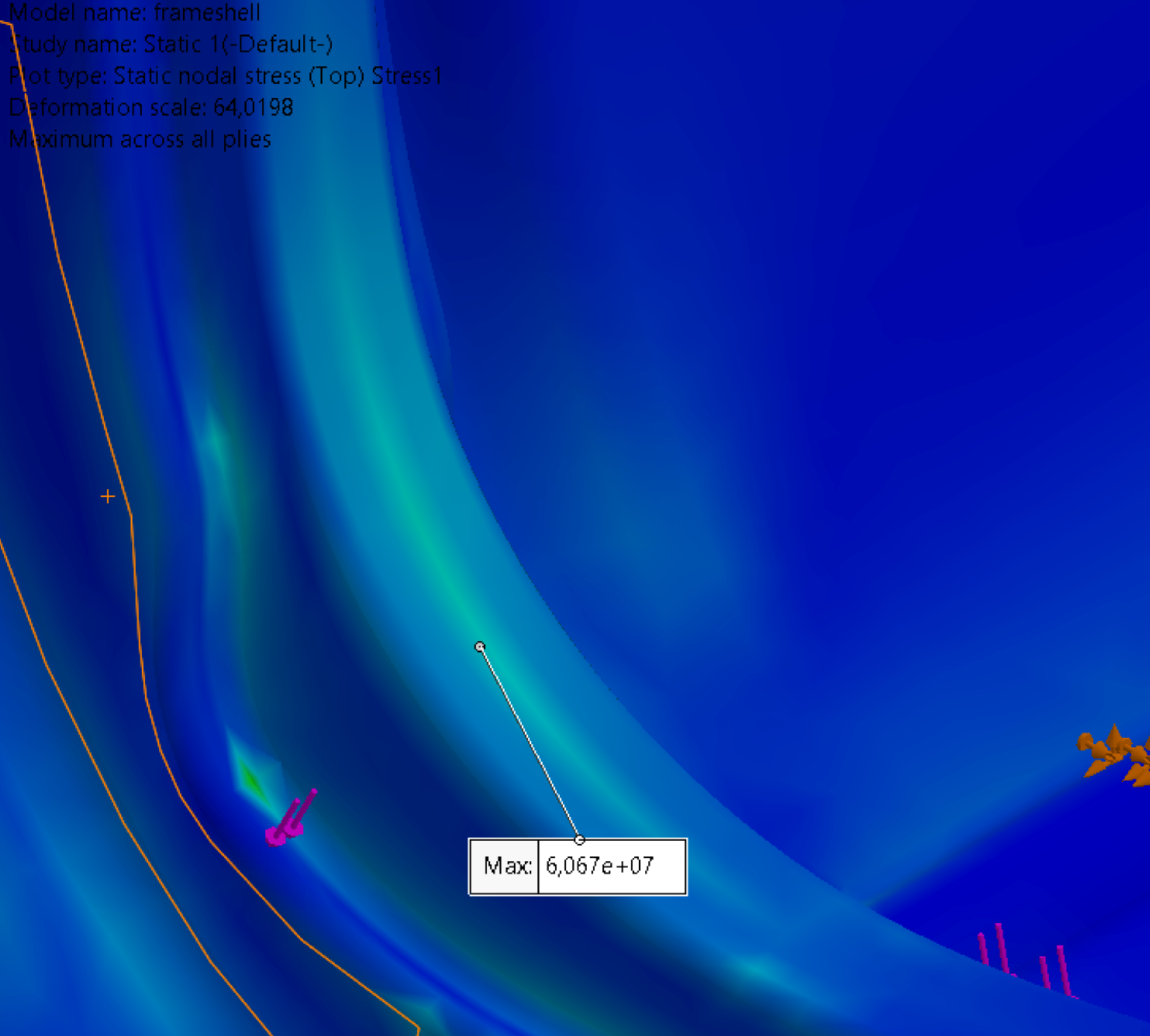
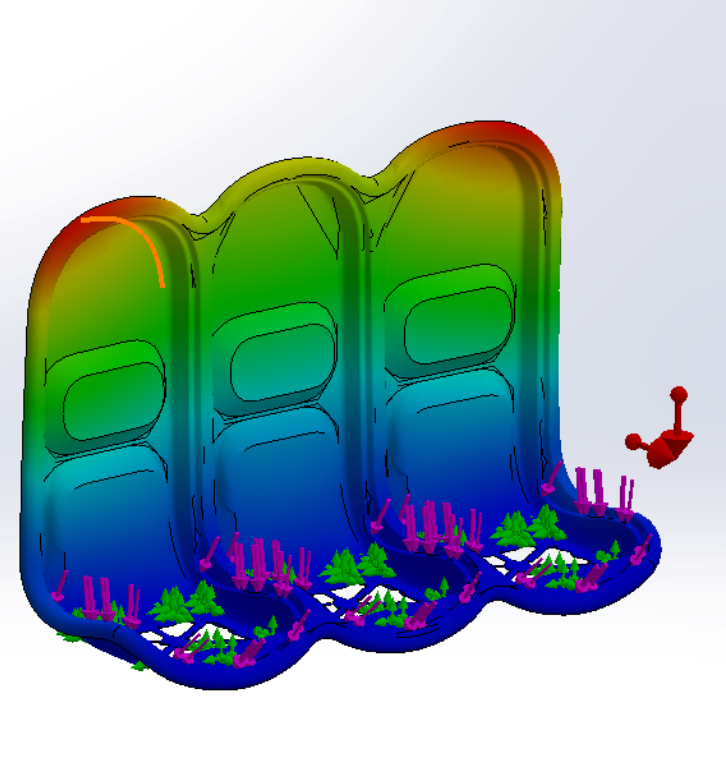
Structural analysis
As a proof of concept, a finite element analysis was performed in Solidworks and utilized the static safety requirement described by the FAA. The results showed no excessive stresses or deformation and proved that it could be possible to make an aircraft seat frame with the CFRTP material; however, dynamic testing is necessary to validate this further.
Weight assesment
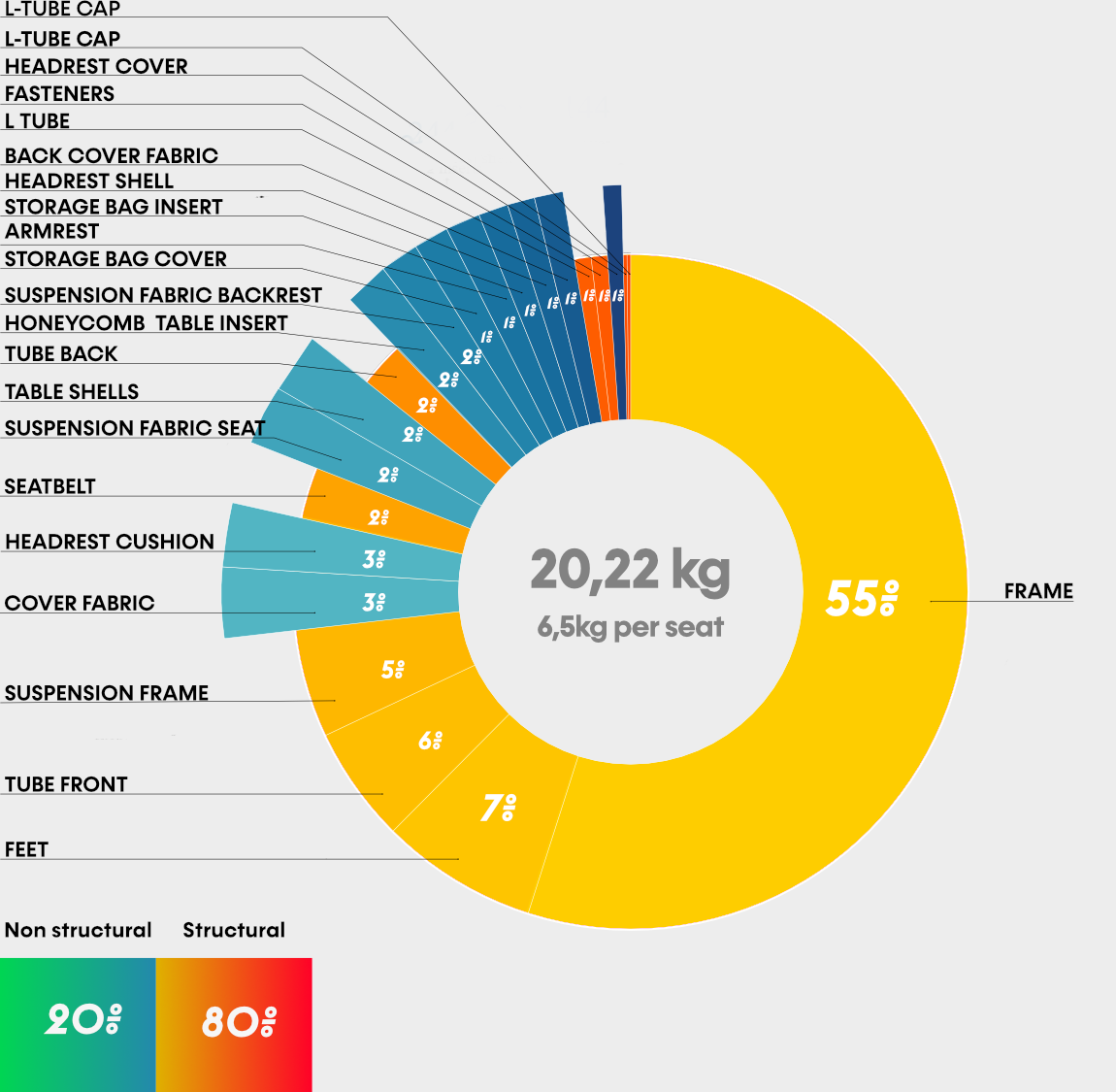
SKY seat weight breakdown (new)
Reference seat weight breakdown (old)

Based on the CAD design, the volume of the parts and the material density, the weight of the complete bench seat was estimated to be 20.22 kg.
One seat has an estimated weight of 6.7 kg. This weight includes the tray table and the storage bag for personal items. If the chair is stripped down to its essentials and these parts are removed, we end up with a starting weight of 6.3 kg.
With this weight of about 6.5 kg, the seat falls between 4 and 8 kg, And show that optimization of the frame, which accounts for 55% of the total weight, has the most potential for further weight reduction.
© Orelio De Jonghe 2023
All Rights Reserved.